d(GA x TC)(n) microsatellite DNA sequences enhance homologous DNA recombination in SV40 minichromosomes
- PMID: 11095670
- PMCID: PMC115175
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/28.23.4617
d(GA x TC)(n) microsatellite DNA sequences enhance homologous DNA recombination in SV40 minichromosomes
Abstract
The genomic distribution of the abundant eukaryotic d(GA x TC)(n) DNA microsatellite suggests that it could contribute to DNA recombination. Here, it is shown that this type of microsatellite DNA sequence enhances DNA recombination in SV40 minichromosomes, the rate of homologous DNA recombination increasing by as much as two orders of magnitude in the presence of a d(GA x TC)(22) sequence. This effect depends on the region of the SV40 genome at which the d(GA x TC)(22) sequence is cloned. It is high when the sequence is located proximal to the SV40 control region but no effect is observed when located 3.5 kb away from the SV40 ori. These results indicate that the recombination potential of d(GA x TC)(n) sequences is likely linked to DNA replication and/or transcription. The potential contribution of the structural properties of d(GA x TC)(n) sequences to this effect is discussed.
Figures

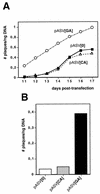

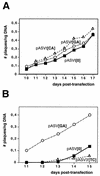
References
-
- Manor H., Rao,B.S. and Martin,R.G. (1988) Abundance and degree of dispersion of genomic d(GA)n.d(TC)n sequences. J. Mol. Evol., 27, 96–101. - PubMed
-
- Birnboim H.C., Sederoff,R.R. and Paterson,M.C. (1979) Distribution of polypyrimidine·polypurine segments in DNA from diverse organisms. Eur. J. Biochem., 98, 301–307. - PubMed
-
- Collier D.A., Griffin,J.A. and Wells,R.D. (1988) Non-B right-handed DNA conformations of homopurine.homopyrimidine sequences in the murine immunoglobulin Cα switch region. J. Biol. Chem., 263, 7397–7405. - PubMed
-
- Richards J.E., Gilliam,A.C., Shen,A., Tucker,P.W. and Blattner,F.R. (1983) Unusual sequences in the murine immunoglobulin µ–δ heavy-chain region. Nature, 306, 483–487. - PubMed
-
- Weinreb A., Collier,D.A., Birshtein,B.K. and Wells,R.D. (1990) Left-handed Z-DNA and intramolecular triplex formation at the site of an unequal sister chromatid exchange. J. Biol. Chem., 265, 1352–1359. - PubMed

