Species specificity of human RPA in simian virus 40 DNA replication lies in T-antigen-dependent RNA primer synthesis
- PMID: 11095685
- PMCID: PMC115162
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/28.23.4742
Species specificity of human RPA in simian virus 40 DNA replication lies in T-antigen-dependent RNA primer synthesis
Abstract
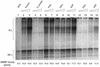
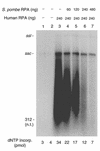
Replication protein A (RPA) is a three-subunit protein complex with multiple functions in DNA replication. Previous study indicated that human RPA (h-RPA) could not be replaced by Schizosaccharomyces pombe RPA (sp-RPA) in simian virus 40 (SV40) replication, suggesting that h-RPA may have a specific function in SV40 DNA replication. To understand the specificity of h-RPA in replication, we prepared heterologous RPAs containing the mixture of human and S.pombe subunits and compared these preparations for various enzymatic activities. Heterologous RPAs containing two human subunits supported SV40 DNA replication, whereas those containing only one human subunit poorly supported DNA replication, suggesting that RPA complex requires at least two human subunits to support its function in SV40 DNA replication. All heterologous RPAs effectively supported single-stranded (ss)DNA binding activity and an elongation of a primed DNA template catalyzed by DNA polymerase (pol) alpha and delta. A strong correlation between SV40 DNA replication activity and large tumor antigen (T-ag)-dependent RNA primer synthesis by pol alpha-primase complex was observed among the heterologous RPAs. Furthermore, T-ag showed a strong interaction with 70- and 34-kDa subunits from human, but poorly interacted with their S.pombe counterparts, indicating that the specificity of h-RPA is due to its role in RNA primer synthesis. In the SV40 replication reaction, the addition of increasing amounts of sp-RPA in the presence of fixed amount of h-RPA significantly reduced overall DNA synthesis, but increased the size of lagging strand, supporting a specific role for h-RPA in RNA primer synthesis. Together, these results suggest that the specificity of h-RPA in SV40 replication lies in T-ag-dependent RNA primer synthesis.
Figures



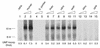


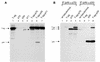
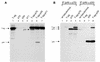
References
-
- Wobbe C.R., Weissbach,L., Borowiec,J.A., Dean,F.B., Murakami,Y., Bullock,P. and Hurwitz,J. (1987) Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA., 82, 5710–5714.
-
- Brill S.J. and Stillman,B. (1991) Genes Dev., 5, 1589–1600. - PubMed
-
- Erdile L.F., Heyer,W.-D., Kolodner,R. and Kelly,T.J. (1991) J. Biol. Chem., 266, 12090–12098. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

