The autoproteolysis of Lactococcus lactis lactocepin III affects its specificity towards beta-casein
- PMID: 11097880
- PMCID: PMC92434
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.12.5134-5140.2000
The autoproteolysis of Lactococcus lactis lactocepin III affects its specificity towards beta-casein
Abstract
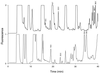
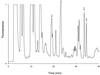
The effect of autoproteolysis of Lactococcus lactis lactocepin III on its specificity towards beta-casein was investigated. beta-Casein degradation was performed by using either an autolysin-defective derivative of L. lactis MG1363 carrying the proteinase genes of L. lactis SK11, which was unable to transport oligopeptides, or autoproteolyzed enzyme purified from L. lactis SK11. Comparison of the peptide pools by high-performance liquid chromatography analysis revealed significant differences. To analyze these differences in more detail, the peptides released by the cell-anchored proteinase were identified by on-line coupling of liquid chromatography to mass spectrometry. More than 100 oligopeptides were released from beta-casein by the cell-anchored proteinase. Analysis of the cleavage sites indicated that the specificity of peptide bond cleavage by the cell-anchored proteinase differed significantly from that of the autoproteolyzed enzyme.
Figures

References
-
- Chopin A. Organization and regulation of genes for amino acid biosynthesis of lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1993;12:21–38. - PubMed
-
- de Vos W M, Vos P, de Haard H, Boerrigter I. Cloning and expression of the Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris SK11 gene encoding an extracellular serine proteinase. Gene. 1989;85:169–176. - PubMed
-
- Dornan S, Collins M A. High efficiency electroporation of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis LM0230 with plasmid pGB301. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1990;11:62–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

