Physiological study of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus strains in a novel chemically defined medium
- PMID: 11097906
- PMCID: PMC92460
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.12.5306-5311.2000
Physiological study of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus strains in a novel chemically defined medium
Abstract
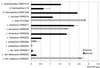
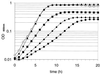
We developed a chemically defined medium called milieu proche du lait (MPL), in which 22 Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus (L. bulgaricus) strains exhibited growth rates ranging from 0.55 to 1 h(-1). MPL can also be used for cultivation of other lactobacilli and Streptococcus thermophilus. The growth characteristics of L. bulgaricus in MPL containing different carbon sources were determined, including an initial characterization of the phosphotransferase system transporters involved. For the 22 tested strains, growth on lactose was faster than on glucose, mannose, and fructose. Lactose concentrations below 0.4% were limiting for growth. We isolated 2-deoxyglucose-resistant mutants from strains CNRZ397 and ATCC 11842. CNRZ397-derived mutants were all deficient for glucose, fructose, and mannose utilization, indicating that these three sugars are probably transported via a unique mannose-specific-enzyme-II-like transporter. In contrast, mutants of ATCC 11842 exhibited diverse phenotypes, suggesting that multiple transporters may exist in that strain. We also developed a protein labeling method and verified that exopolysaccharide production and phage infection can occur in MPL. The MPL medium should thus be useful in conducting physiological studies of L. bulgaricus and other lactic acid bacteria under well controlled nutritional conditions.
Figures

References
-
- Accolas J-P, Chopin M-C. Bacteriophages of lactic starters detection and enumeration. In: Bourgeois C M, Leveau J Y, editors. Techniques d'analyse et de contrôle dans les industries agroalimentaires. Le contrôle microbiologique. Vol. 3. Paris, France: Technique et Documentation APRIA; 1980. pp. 159–173.
-
- Alais C. Science du lait. Principes des techniques laitières. 4th ed. Paris, France: Sepaic; 1984.
-
- Buchanan R E, Gibbons N E, editors. Bergey's manual of determinative bacteriology. 8th ed. Baltimore, Md: The Williams & Wilkins Co.; 1974.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

