Rapid method for coextraction of DNA and RNA from natural environments for analysis of ribosomal DNA- and rRNA-based microbial community composition
- PMID: 11097934
- PMCID: PMC92488
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.12.5488-5491.2000
Rapid method for coextraction of DNA and RNA from natural environments for analysis of ribosomal DNA- and rRNA-based microbial community composition
Abstract
A rapid protocol for the extraction of total nucleic acids from environmental samples is described. The method facilitates concomitant assessment of microbial 16S rRNA diversity by PCR and reverse transcription-PCR amplification from a single extraction. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis microbial community analysis differentiated the active component (rRNA derived) from the total bacterial diversity (ribosomal DNA derived) down the horizons of an established grassland soil.
Figures

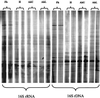
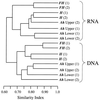
References
-
- Blumberg D D. Creating a ribonuclease-free environment. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:20–24. - PubMed
-
- Duarte G F, Rosado A S, Seldin L, KeijzerWolters A C, van Elsas J D. Extraction of ribosomal RNA and genomic DNA from soil for studying the diversity of the indigenous bacterial community. J Microb Methods. 1998;32:21–29.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

