The interaction of titin and alpha-actinin is controlled by a phospholipid-regulated intramolecular pseudoligand mechanism
- PMID: 11101506
- PMCID: PMC305858
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.23.6331
The interaction of titin and alpha-actinin is controlled by a phospholipid-regulated intramolecular pseudoligand mechanism
Abstract
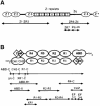
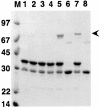
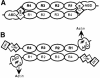
The assembly of stable cytoskeletal structures from dynamically recycled molecules requires developmental and spatial regulation of protein interactions. In muscle, titin acts as a molecular ruler organizing the actin cytoskeleton via interactions with many sarcomeric proteins, including the crosslinking protein alpha-actinin. An interaction between the C-terminal domain of alpha-actinin and titin Z-repeat motifs targets alpha-actinin to the Z-disk. Here we investigate the cellular regulation of this interaction. alpha-actinin is a rod shaped head-to-tail homodimer. In contrast to C-terminal fragments, full-length alpha-actinin does not bind Z-repeats. We identify a 30-residue Z-repeat homologous sequence between the actin-binding and rod regions of alpha-actinin that binds the C-terminal domain with nanomolar affinity. Thus, Z-repeat binding is prevented by this 'pseudoligand' interaction between the subunits of the alpha-actinin dimer. This autoinhibition is relieved upon binding of the Z-disk lipid phosphatidylinositol-bisphosphate to the actin-binding domain. We suggest that this novel mechanism is relevant to control the site-specific interactions of alpha-actinin during sarcomere assembly and turnover. The intramolecular contacts defined here also constrain a structural model for intrasterical regulation of all alpha-actinin isoforms.
Figures





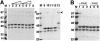

References
-
- Astier C., Raynaud,F., Lebart,M.C., Roustan,C. and Benyamin,Y. (1998) Binding of a native titin fragment to actin is regulated by PIP2. FEBS Lett., 429, 95–98. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson R.A., Joseph,C., Dal Piaz,F., Birolo,L., Stier,G., Pucci,P. and Pastore,A. (2000) Binding of α-actinin to titin: implications for Z-disk assembly. Biochemistry, 39, 5255–5264. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F.M., Brent,R., Kingston,R.E., Moore,D.D., Seidman,J.G., Smith,J.A. and Struhl,K. (1987) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, NY.
-
- Beckerle M.C. (1997) Zyxin: zinc fingers at sites of cell adhesion. BioEssays, 19, 949–957. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard A., Ohanian,V. and Critchley,D. (1989) The structure and function of α-actinin. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil., 10, 280–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

