The peroxisomal membrane protein Pex13p shows a novel mode of SH3 interaction
- PMID: 11101511
- PMCID: PMC305852
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.23.6382
The peroxisomal membrane protein Pex13p shows a novel mode of SH3 interaction
Abstract
Src homology 3 (SH3) domains are small non-catalytic protein modules capable of mediating protein-protein interactions by binding to proline-X-X-proline (P-X-X-P) motifs. Here we demonstrate that the SH3 domain of the integral peroxisomal membrane protein Pex13p is able to bind two proteins, one of which, Pex5p, represents a novel non-P-X-X-P ligand. Using alanine scanning, two-hybrid and in vitro interaction analysis, we show that an alpha-helical element in Pex5p is necessary and sufficient for SH3 interaction. Sup pressor analysis using Pex5p mutants located in this alpha-helical element allowed the identification of a unique site of interaction for Pex5p on the Pex13p-SH3 domain that is distinct from the classical P-X-X-P binding pocket. On the basis of a structural model of the Pex13p-SH3 domain we show that this interaction probably takes place between the RT- and distal loops. Thus, the Pex13p-SH3-Pex5p interaction establishes a novel mode of SH3 interaction.
Figures





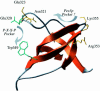
References
-
- Albertini M., Rehling,P., Erdmann,R., Girzalsky,W., Kiel,J.A., Veenhuis,M. and Kunau,W.H. (1997) Pex14p, a peroxisomal membrane protein binding both receptors of the two PTS-dependent import pathways. Cell, 89, 83–92. - PubMed
-
- Arold S., O’Brien,R., Franken,P., Strub,M.P., Hoh,F., Dumas,C. and Ladbury,J.E. (1998) RT loop flexibility enhances the specificity of Src family SH3 domains for HIV-1 Nef. Biochemistry, 37, 14683–14691. - PubMed
-
- Blatch G.L. and Lassle,M. (1999) The tetratricopeptide repeat: a structural motif mediating protein–protein interactions. BioEssays, 21, 932–939. - PubMed
-
- Brocard C., Kragler,F., Simon,M.M., Schuster,T. and Hartig,A. (1994) The tetratricopeptide repeat-domain of the PAS10 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is essential for binding the peroxisomal targeting signal-SKL. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 204, 1016–1022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

