SRP-dependent co-translational targeting and SecA-dependent translocation analyzed as individual steps in the export of a bacterial protein
- PMID: 11101515
- PMCID: PMC305875
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.23.6419
SRP-dependent co-translational targeting and SecA-dependent translocation analyzed as individual steps in the export of a bacterial protein
Abstract
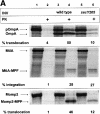
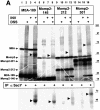
Recently it has been recognized that the signal recognition particle (SRP) of Escherichia coli represents a specific targeting device for hydrophobic inner membrane proteins. It has remained unclear, however, whether the bacterial SRP functions in concert with SecA, which is required for the translocation of secretory proteins across the inner membrane. Here, we have analyzed a hybrid protein constructed by fusing the signal anchor sequence of an SRP-dependent inner membrane protein (MtlA) to the mature part of an exclusively SecA-requiring secretory protein (OmpA). We show that the signal anchor sequence of MtlA confers the novel properties onto nascent chains of OmpA of being co-translationally recognized and targeted to SecY by SRP. Once targeted to SecY, ribosome-associated nascent chains of the hybrid protein, however, remain untranslocated unless SecA is present. These results indicate that SRP and SecA cooperate in a sequential, non-overlapping manner in the topogenesis of those membrane proteins which, in addition to a signal anchor sequence, harbor a substantial hydrophilic domain to be translocated into the periplasm.
Figures









References
-
- Behrmann M., Koch,H.G., Hengelage,T., Wieseler,B., Hoffschulte,H.K. and Muller,M. (1998) Requirements for the translocation of elongation-arrested, ribosome-associated OmpA across the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 13898–13904. - PubMed
-
- Crowley K.S., Reinhart,G.D. and Johnson,A.E. (1993) The signal sequence moves through a ribosomal tunnel into a noncytoplasmic aqueous environment at the ER membrane early in translocation. Cell, 73, 1101–1115. - PubMed
-
- Crowley K.S., Liao,S., Worrel.,V.E., Reinhart,G.D. and Johnson,A.E. (1994) Secretory proteins move through the endoplasmic reticulum membrane via an aqueous, gated pore. Cell, 78, 461–471. - PubMed
-
- de Gier J.W., Mansournia,P., Valent,Q.A., Phillips,G.J., Luirink,J. and von Heijne,G. (1996) Assembly of a cytoplasmic membrane protein in Escherichia coli is dependent on the signal recognition particle. FEBS Lett., 399, 307–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

