Hsp70-RAP46 interaction in downregulation of DNA binding by glucocorticoid receptor
- PMID: 11101523
- PMCID: PMC305849
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.23.6508
Hsp70-RAP46 interaction in downregulation of DNA binding by glucocorticoid receptor
Abstract
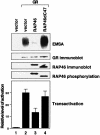
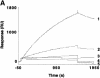
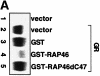
Receptor-associating protein 46 (RAP46) is a cochaperone that regulates the transactivation function of several steroid receptors. It is transported into the nucleus by a liganded glucocorticoid receptor where it downregulates DNA binding and transactivation by this receptor. The N- and C-termini of RAP46 are both implicated in its negative regulatory function. In metabolic labelling experiments, we have shown that the N-terminus of RAP46 is modified by phosphorylation, but this does not contribute to the downregulation of glucocorticoid receptor activity. However, deletion of a sequence that binds 70 kDa heat shock protein (Hsp70) and the constitutive isoform of Hsp70 (Hsc70) at the C-terminus of RAP46 abrogated its negative regulatory action. Surface plasmon resonance studies showed that RAP46 binds the glucocorticoid receptor only when it has interacted with Hsp70/Hsc70, and confocal immunofluorescence analyses revealed a nuclear transport of Hsp70/Hsc70 by the liganded receptor. Together these findings demonstrate an important contribution of Hsp70/Hsc70 in the binding of RAP46 to the glucocorticoid receptor and suggest a role for this molecular chaperone in the RAP46-mediated downregulation of glucocorticoid receptor activity.
Figures






References
-
- Anfinsen C.B. (1973) Principles that govern the folding of protein chains. Science, 181, 223–230. - PubMed
-
- Bohen S.P., Kralli,A. and Yamamoto,K.R. (1995) Hold’em and fold’em: chaperones and signal transduction. Science, 268, 1303–1304. - PubMed
-
- Bresnick E.H., Dalman,F.C., Sanchez,E.R. and Pratt,W.B. (1989) Evidence that the 90-kDa heat shock protein is necessary for the steroid binding conformation of the L cell glucocorticoid receptor. J. Biol. Chem., 264, 4992–4997. - PubMed
-
- Buchner J. (1999) Hsp90 & Co.—a holding for folding. Trends Biochem. Sci., 24, 136–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

