Functional analysis of the human CDC5L complex and identification of its components by mass spectrometry
- PMID: 11101529
- PMCID: PMC305846
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.23.6569
Functional analysis of the human CDC5L complex and identification of its components by mass spectrometry
Abstract
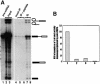
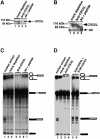
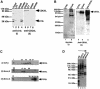
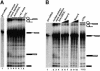
Recently, we identified proteins that co-purify with the human spliceosome using mass spectrometry. One of the identified proteins, CDC5L, corresponds to the human homologue of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe CDC5(+) gene product. Here we show that CDC5L is part of a larger multiprotein complex in HeLa nuclear extract that incorporates into the spliceosome in an ATP-dependent step. We also show that this complex is required for the second catalytic step of pre-mRNA splicing. Immunodepletion of the CDC5L complex from HeLa nuclear extract inhibits the formation of pre-mRNA splicing products in vitro but does not prevent spliceosome assembly. The first catalytic step of pre-mRNA splicing is less affected by immunodepleting the complex. The purified CDC5L complex in HeLa nuclear extract restores pre-mRNA splicing activity when added to extracts that have been immunodepleted using anti-CDC5L antibodies. Using mass spectrometry and database searches, the major protein components of the CDC5L complex have been identified. This work reports a first purification and characterization of a functional, human non-snRNA spliceosome subunit containing CDC5L and at least five additional protein factors.
Figures

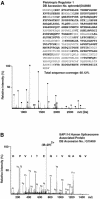
References
-
- Bennett M. and Reed,R. (1993) Correspondence between a mammalian spliceosome component and an essential yeast splicing factor. Science, 262, 105–108. - PubMed
-
- Bennett M., Michaud,S., Kingston,J. and Reed,R. (1992) Protein components specifically associated with prespliceosome and spliceosome complexes. Genes Dev., 6, 1986–2000. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein H.S. and Coughlin,S.R. (1997) A putative human transcription factor implicated in mitogen-activated signaling. J. Biol. Chem., 272, 5833–5837. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein H.S. and Coughlin,S.R. (1998) A mammalian homolog of fission yeast CDC5 regulates G2 progression and mitotic entry. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 4666–4671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

