Growth/differentiation factor-15/macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 is a novel trophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons in vivo
- PMID: 11102463
- PMCID: PMC6773071
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-23-08597.2000
Growth/differentiation factor-15/macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 is a novel trophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons in vivo
Abstract
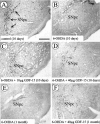
Transforming growth factor-betas (TGF-betas) constitute an expanding family of multifunctional cytokines with prominent roles in development, cell proliferation, differentiation, and repair. We have cloned, expressed, and raised antibodies against a distant member of the TGF-betas, growth/differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15). GDF-15 is identical to macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1). GDF-15/MIC-1 mRNA and protein are widely distributed in the developing and adult CNS and peripheral nervous systems, including choroid plexus and CSF. GDF-15/MIC-1 is a potent survival promoting and protective factor for cultured and iron-intoxicated dopaminergic (DAergic) neurons cultured from the embryonic rat midbrain floor. The trophic effect of GDF-15/MIC-1 was not accompanied by an increase in cell proliferation and astroglial maturation, suggesting that GDF-15/MIC-1 probably acts directly on neurons. GDF-15/MIC-1 also protects 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-lesioned nigrostriatal DAergic neurons in vivo. Unilateral injections of GDF-15/MIC-1 into the medial forebrain bundle just above the substantia nigra (SN) and into the left ventricle (20 microgram each) immediately before a 6-OHDA injection (8 microgram) prevented 6-OHDA-induced rotational behavior and significantly reduced losses of DAergic neurons in the SN. This protection was evident for at least 1 month. Administration of 5 microgram of GDF-15/MIC-1 in the same paradigm also provided significant neuroprotection. GDF-15/MIC-1 also promoted the serotonergic phenotype of cultured raphe neurons but did not support survival of rat motoneurons. Thus, GDF-15/MIC-1 is a novel neurotrophic factor with prominent effects on DAergic and serotonergic neurons. GDF-15/MIC-1 may therefore have a potential for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and disorders of the serotonergic system.
Figures




References
-
- Aebischer P, Schluep M, Delon N, Joseph JM, Hirt L, Heyd B, Goddard M, Hammang JP, Zurn AD, Kato AC, Regli F, Baetge EE. Intrathecal delivery of CNTF using encapsulated genetically modified xenogeneic cells in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Nat Med. 1996;2:696–699. - PubMed
-
- Alexi T, Hefti F. Trophic actions of transforming growth factor alpha on mesencephalic neurons developing in culture. Neuroscience. 1993;55:903–918. - PubMed
-
- Behar T, McMorris FA, Novotny EA, Barker JL, Dubois-Dalc M. Growth and differentiation properties of O-2A progenitors purified from rat cerebral hemispheres. J Neurosci Res. 1988;21:168–180. - PubMed
-
- Bieger S, Unsicker K. Functions of fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) in the nervous system. In: Bell C, editor. Chemical factors in neuronal growth, degeneration and repair. Elsevier; Amsterdam: 1996. pp. 339–361.
-
- Bootcov MR, Bauskin AR, Valenzuela SM, Moore AG, Bansal M, He XY, Zhang HP, Donnellan M, Mahler S, Pryor K, Walsh BJ, Nicholson RC, Fairlie WD, Por SP, Robbins JM, Breit SN. Mic-1, a novel macrophage inhibitory cytokine, is a divergent member of the TGF-β superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:11514–11519. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
