GABA spillover from single inhibitory axons suppresses low-frequency excitatory transmission at the cerebellar glomerulus
- PMID: 11102470
- PMCID: PMC6773066
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-23-08651.2000
GABA spillover from single inhibitory axons suppresses low-frequency excitatory transmission at the cerebellar glomerulus
Abstract
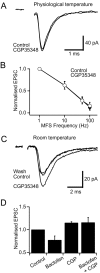
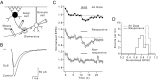
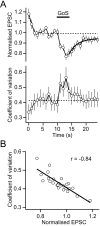
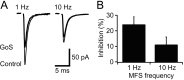
GABA type B receptors (GABA(B)-Rs) are present on excitatory terminals throughout the CNS, but surprisingly little is known about their role in modulating neurotransmission under physiological conditions. We have investigated activation of GABA(B)-Rs on excitatory terminals within the cerebellar glomerulus, a structure where glutamatergic excitatory and GABAergic inhibitory terminals are in close apposition and make axodendritic synapses onto granule cells. Application of the GABA(B)-R agonist baclofen depressed evoked mossy fiber EPSCs by 54% at 1 Hz. The amplitude of miniature EPSCs recorded in tetrodotoxin was unchanged in the presence of baclofen, but the frequency was significantly reduced, indicating a purely presynaptic action of baclofen under our recording conditions. At physiological temperature (37 degrees C) presynaptic GABA(B)-Rs were not tonically activated by spontaneous GABA release from Golgi cells, which fire at approximately 8 Hz in slices at this temperature. However, tonic activation could be induced by blocking GABA uptake or by lowering temperature. GABA(B)-Rs were activated at physiological temperature when Golgi cell firing was increased above the basal level by stimulating a single inhibitory Golgi cell input at 50 Hz, suppressing the mossy fiber-evoked EPSC by 24% at 1 Hz. Furthermore, glutamate release was selectively inhibited at low-frequency mossy fiber inputs (<10 Hz) during Golgi cell stimulation. Our findings suggest that GABA spillover in the glomerulus modulates sensory input to the cerebellar cortex.
Figures




References
-
- Abbott LF, Varela JA, Sen K, Nelson SB. Synaptic depression and cortical gain control. Science. 1997;275:220–224. - PubMed
-
- Aroniadou-Anderjaska V, Zhou F-M, Priest CA, Ennis M, Shipley MT. Tonic and synaptically evoked presynaptic inhibition of sensory input to the rat olfactory bulb via GABAB heteroreceptors. J Neurophysiol. 2000;84:1194–1203. - PubMed
-
- Barbour B, Häusser M. Intersynaptic diffusion of neurotransmitter. Trends Neurosci. 1997;20:377–384. - PubMed
-
- Bean BP. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989;340:153–156. - PubMed
-
- Brenowitz S, David J, Trussell L. Enhancement of synaptic efficacy by presynaptic GABA(B) receptors. Neuron. 1998;20:135–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
