Dendritic and axonal targeting of type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor is regulated by homer1 proteins and neuronal excitation
- PMID: 11102477
- PMCID: PMC6773061
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-23-08710.2000
Dendritic and axonal targeting of type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor is regulated by homer1 proteins and neuronal excitation
Abstract
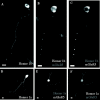
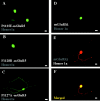
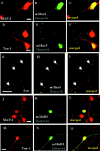
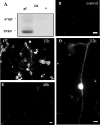
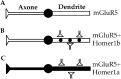
The physiological actions of neurotransmitter receptors are intimately linked to their proper neuronal compartment localization. Here we studied the effect of the metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR)-interacting proteins, Homer1a, b, and c, in the targeting of mGluR5 in neurons. We found that mGluR5 was exclusively localized in cell bodies when transfected alone in cultured cerebellar granule cells. In contrast, mGluR5 was found also in dendrites when coexpressed with Homer1b or Homer1c, and in both dendrites and axons when cotransfected with Homer1a. In dendrites, cotransfected mGluR5 and Homer1b/c formed clusters that colocalized with the synaptic marker synaptophysin. Interestingly when transfected alone, the Homer proteins were also translocated to neurites but did not form such clusters. Depolarization of the neurons with a mixture of ionotropic glutamate receptor agonists, NMDA and kainate, or potassium channel blockers, tetraethylammonium and 4-aminopyridine, induced transient expression of endogenous Homer1a and persistent neuritic localization of transfected mGluR5 even long after degradation of Homer1a. These results suggest that Homer1a/b/c proteins are involved in the targeting of mGluR5 to dendritic synaptic sites and/or axons and that this effect can be regulated by neuronal activity. Because the activity-dependent effect of endogenous Homer1a was also long-lasting, the axonal targeting of mGluR5 by this protein is likely to play an important role in synaptic plasticity.
Figures

References
-
- Abe T, Sugihara H, Nawa H, Shigemoto R, Mizuno N, Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 coupled to inositol phosphate/Ca2+ signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:13361–13368. - PubMed
-
- Aiba A, Kano M, Chen C, Stanton ME, Fox GD, Herrup K, Zwingman TA, Tonegawa S. Deficient cerebellar long-term depression and impaired motor learning in mGluR1 mutant mice. Cell. 1994;79:377–388. - PubMed
-
- Alagarsamy S, Marino MJ, Rouse ST, Gereau RW, Heinemann SF, Conn PJ. Activation of NMDA receptors reverses desensitization of mGluR5 in native and recombinant systems. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:234–240. - PubMed
-
- Ango F, Albani-Torregrossa S, Joly C, Robbe D, Michel JM, Pin JP, Bockaert J, Fagni L. A simple method to transfer plasmid DNA into neuronal primary cultures: functional expression of the mGlu5 receptor in cerebellar granule cells. Neuropharmacology. 1999;38:793–803. - PubMed
-
- Anwyl R. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: electrophysiological properties and role in plasticity. Brain Res Rev. 1999;29:83–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
