Genomic expression programs in the response of yeast cells to environmental changes
- PMID: 11102521
- PMCID: PMC15070
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.11.12.4241
Genomic expression programs in the response of yeast cells to environmental changes
Abstract
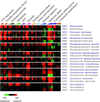
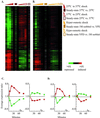
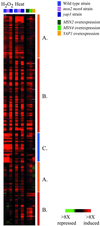
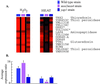
We explored genomic expression patterns in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae responding to diverse environmental transitions. DNA microarrays were used to measure changes in transcript levels over time for almost every yeast gene, as cells responded to temperature shocks, hydrogen peroxide, the superoxide-generating drug menadione, the sulfhydryl-oxidizing agent diamide, the disulfide-reducing agent dithiothreitol, hyper- and hypo-osmotic shock, amino acid starvation, nitrogen source depletion, and progression into stationary phase. A large set of genes (approximately 900) showed a similar drastic response to almost all of these environmental changes. Additional features of the genomic responses were specialized for specific conditions. Promoter analysis and subsequent characterization of the responses of mutant strains implicated the transcription factors Yap1p, as well as Msn2p and Msn4p, in mediating specific features of the transcriptional response, while the identification of novel sequence elements provided clues to novel regulators. Physiological themes in the genomic responses to specific environmental stresses provided insights into the effects of those stresses on the cell.
Figures
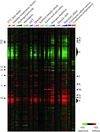
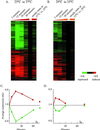
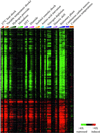
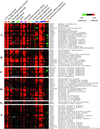
Comment in
-
It's the data!Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Jan 1;21(1):4-6. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-07-0575. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20048255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey TL, Elkan C. Conference on Intelligent systems for Molecular Biology. Menlo Park, CA: AAAl Press; 1994. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers; pp. 28–36. - PubMed
-
- Ball CA, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Harris MA, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Scafe CR, Sherlock G, Binkley G, Jin H, Kaloper M, Orr SD, Schroeder M, Weng S, Zhu Y, Botstein D, Cherry JM. Integrating functional genomic information into the Saccharomyces genome database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28:77–80. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cox JS, Shamu CE, Walter P. Transcriptional induction of genes encoding endoplasmic reticulum resident proteins requires a transmembrane protein kinase. Cell. 1993;73:1197–1206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

