An overview of the structures of protein-DNA complexes
- PMID: 11104519
- PMCID: PMC138832
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2000-1-1-reviews001
An overview of the structures of protein-DNA complexes
Abstract
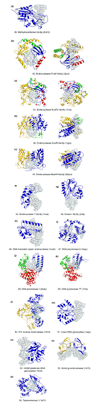
On the basis of a structural analysis of 240 protein-DNA complexes contained in the Protein Data Bank (PDB), we have classified the DNA-binding proteins involved into eight different structural/functional groups, which are further classified into 54 structural families. Here we present this classification and review the functions, structures and binding interactions of these protein-DNA complexes.
Figures







References
-
- Harrison SC. A structural taxonomy of DNA-binding domains. . Nature. 1991;353:715–719. - PubMed
-
- Luisi BF. DNA-protein interaction at high resolution. In DNA-Protein Structural Interactions Edited by Lilley DMJ New York: Oxford University Press, 1995:1–48.
-
- Frishman D, Mewes H-W. PEDANTic genome analysis. Trends Genet. 1997;13:415–416.
-
- Bernstein FC, Koetzler TF, Williams GJB, Meyer EF, Brice MD, Rogers JR, Kennard O, Shimanouchi T, Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based achival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977;112:535–542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

