Follicular B helper T cells express CXC chemokine receptor 5, localize to B cell follicles, and support immunoglobulin production
- PMID: 11104797
- PMCID: PMC2193094
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.192.11.1545
Follicular B helper T cells express CXC chemokine receptor 5, localize to B cell follicles, and support immunoglobulin production
Abstract
Chemokines and their receptors have been identified as major regulators controlling the functional organization of secondary lymphoid organs. Here we show that expression of CXC chemokine receptor 5 (CXCR5), a chemokine receptor required for B cell homing to B cell follicles, defines a novel subpopulation of B helper T cells localizing to follicles. In peripheral blood these cells coexpress CD45RO and the T cell homing CC chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7). In secondary lymphoid organs, CD4(+)CXCR5(+) cells lose expression of CCR7, which allows them to localize to B cell follicles and germinal centers where they express high levels of CD40 ligand (CD40L), a costimulatory molecule required for B cell activation and inducible costimulator (ICOS), a recently identified costimulatory molecule of the CD28 family. Thus, when compared with CD4(+)CD45RO(+)CXCR5(-) cells, CD4(+)CD45RO(+)CXCR5(+) tonsillar T cells efficiently support the production of immunoglobulin (Ig)A and IgG. In contrast, analysis of the memory response revealed that long-lasting memory cells are found within the CD4(+)CD45RO(+)CXCR5(-) population, suggesting that CXCR5(+)CD4 cells represent recently activated effector cells. Based on the characteristic localization within secondary lymphoid organs, we suggest to term these cells "follicular B helper T cells" (T(FH)).
Figures


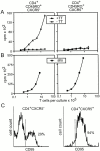
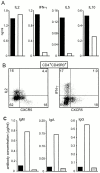
Comment in
-
Follicular homing T helper (Th) cells and the Th1/Th2 paradigm.J Exp Med. 2000 Dec 4;192(11):F31-4. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.11.f31. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 11104811 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Butcher E.C., Picker L.J. Lymphocyte homing and homeostasis. Science. 1996;272:60–66. - PubMed
-
- Cyster J.G. Chemokines and cell migration in secondary lymphoid organs. Science. 1999;286:2098–2102. - PubMed
-
- Förster R., Schubel A., Breitfeld D., Kremmer E., Renner-Müller I., Wolf E., Lipp M. CCR7 coordinates the primary immune response by establishing functional microenvironments in secondary lymphoid organs. Cell. 1999;99:23–33. - PubMed
-
- Förster R., Mattis E.A., Kremmer E., Wolf E., Brem G., Lipp M. A putative chemokine receptor, BLR1, directs B cell migration to defined lymphoid organs and specific anatomic compartments of the spleen. Cell. 1996;87:1037–1047. - PubMed
-
- Ansel K.M., Ngo V.N., Hyman P.L., Luther S.A., Forster R., Sedgwick J.D., Browning J.L., Lipp M., Cyster J.G. A chemokine-driven positive feedback loop organizes lymphoid follicles. Nature. 2000;406:309–314. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

