CXC chemokine receptor 5 expression defines follicular homing T cells with B cell helper function
- PMID: 11104798
- PMCID: PMC2193097
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.192.11.1553
CXC chemokine receptor 5 expression defines follicular homing T cells with B cell helper function
Abstract
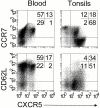
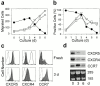
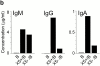
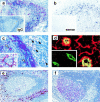
Leukocyte traffic through secondary lymphoid tissues is finely tuned by chemokines. We have studied the functional properties of a human T cell subset marked by the expression of CXC chemokine receptor 5 (CXCR5). Memory but not naive T cells from tonsils are CXCR5(+) and migrate in response to the B cell-attracting chemokine 1 (BCA-1), which is selectively expressed by reticular cells and blood vessels within B cell follicles. Tonsillar CXCR5(+) T cells do not respond to other chemokines present in secondary lymphoid tissues, including secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine (SLC), EBV-induced molecule 1 ligand chemokine (ELC), and stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1). The involvement of tonsillar CXCR5(+) T cells in humoral immune responses is suggested by their localization in the mantle and light zone germinal centers of B cell follicles and by the concomitant expression of activation and costimulatory markers, including CD69, HLA-DR, and inducible costimulator (ICOS). Peripheral blood CXCR5(+) T cells also belong to the CD4(+) memory T cell subset but, in contrast to tonsillar cells, are in a resting state and migrate weakly to chemokines. CXCR5(+) T cells are very inefficient in the production of cytokines but potently induce antibody production during coculture with B cells. These properties portray CXCR5(+) T cells as a distinct memory T cell subset with B cell helper function, designated here as follicular B helper T cells (T(FH)).
Figures

Comment in
-
Follicular homing T helper (Th) cells and the Th1/Th2 paradigm.J Exp Med. 2000 Dec 4;192(11):F31-4. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.11.f31. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 11104811 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Baggiolini M. Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nature. 1998;392:565–568. - PubMed
-
- Loetscher P., Moser B., Baggiolini M. Chemokines and their receptors in lymphocyte traffic and HIV infection. Adv. Immunol. 2000;74:127–180. - PubMed
-
- Murphy P.M., Baggiolini M., Charo I.F., Hebert C.A., Horuk R., Matsushima K., Miller L.H., Oppenheim J.J., Power C.A. International union of pharmacology. XXII. Nomenclature for chemokine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000;52:145–176. - PubMed
-
- Sallusto F., Mackay C.R., Lanzavecchia A. The role of chemokine receptors in primary, effector, and memory immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000;18:593–620. - PubMed
-
- Zlotnik A., Yoshie O. Chemokinesa new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity. 2000;12:121–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

