Selective neuronal necrosis associated with status epilepticus: MR findings
- PMID: 11110535
- PMCID: PMC7974287
Selective neuronal necrosis associated with status epilepticus: MR findings
Abstract
We present the MR imaging findings in an autopsy-proven case of selective neuronal necrosis involving the entire left cerebral hemispheric cortex, left thalamus, and contralateral cerebellum following a period of status epilepticus. Imaging findings include diffusion abnormality on diffusion-weighted images and increased intensity on T2-weighted images in the above-mentioned regions of the brain.
Figures
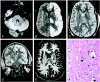
Comment in
-
The status of status: seizures are bad for your brain's health.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000 Nov-Dec;21(10):1782-3. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000. PMID: 11110527 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Childhood status epilepticus and excitotoxic neuronal injury.Pediatr Neurol. 2007 Apr;36(4):253-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2006.12.005. Pediatr Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17437910 Review.
-
Serial EEG and MRI changes in status epilepticus-induced excitotoxic neuronal necrosis.Epileptic Disord. 2011 Dec;13(4):446-51. doi: 10.1684/epd.2011.0472. Epileptic Disord. 2011. PMID: 22258052
-
Rapid alterations in diffusion-weighted images with anatomic correlates in a rodent model of status epilepticus.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000 Nov-Dec;21(10):1841-52. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000. PMID: 11110536 Free PMC article.
-
[An autopsied case of dementia with lewy bodies presenting with hemispheric cerebral cortical atrophy with selective neuronal necrosis after status epilepticus].Brain Nerve. 2012 Sep;64(9):1069-74. Brain Nerve. 2012. PMID: 22941844 Japanese.
-
Fulminant hepatic failure associated with status epilepticus in children: three cases and a review of potential mechanisms.Intensive Care Med. 1994 May;20(5):375-8. doi: 10.1007/BF01720913. Intensive Care Med. 1994. PMID: 7930035 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolated reversible thalamic vasogenic edema following a generalized seizure.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009 May;30(5):e72. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1512. Epub 2009 Feb 4. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009. PMID: 19193757 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Clinical features of neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease with seizures: a systematic literature review.Front Neurol. 2024 Apr 19;15:1387399. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1387399. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38707999 Free PMC article.
-
Review: Hippocampal sclerosis in epilepsy: a neuropathology review.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2014 Aug;40(5):520-43. doi: 10.1111/nan.12150. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24762203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring of acute generalized status epilepticus using multilocal diffusion MR imaging: early prediction of regional neuronal damage.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007 Feb;28(2):321-7. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. PMID: 17297006 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral perfusion alterations during the acute phase of experimental generalized status epilepticus: prediction of survival by using perfusion-weighted MR imaging and histopathology.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005 Jun-Jul;26(6):1563-70. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005. PMID: 15956530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wasterlain CG, Fujikawa DG, Penix LR, Sankar R. Pathophysiological mechanisms of brain damage from status epilepticus. Epilepsia 1993;34:37-153 - PubMed
-
- Fujikawa DG. The temporal evolution of neuronal damage from pilocarpin-induced status epilepticus. Brain Research 1996;725:11-22 - PubMed
-
- Duncan R, Patterson J, Bone I, Wyper DJ. Reversible cerebellar diaschisis in focal epilepsy. Lancet 1987;12:625-626 - PubMed
-
- Fazekas F, Kapeller P, Schmidt R, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy findings after focal status epilepticus. Epilepsia 1995;36:946-949 - PubMed
-
- Wieshman UC, Symms MR, Shorvon SD. Diffusion changes in status epilepticus. Lancet 1997;350:493-494 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
