Dementia, quantitative neuroimaging, and apolipoprotein E genotype
- PMID: 11110538
- PMCID: PMC7974277
Dementia, quantitative neuroimaging, and apolipoprotein E genotype
Abstract
Background and purpose: Quantitative MR imaging differences in an elderly population of subjects with various clinical disorders (including dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia) and disorders of mild cognitive impairment were examined. Potential quantitative MR differences were assessed by presence or absence of the apolipoprotein E (APOE) epsilon4 allele and by level of cognitive deficit.
Methods: One hundred eighty subjects with a diagnosis of dementia or other clinical disorders were identified from an eligible population of 5,677 elderly individuals. Age, duration of disease, and head size (where appropriate) were considered as covariates. APOE genotype was determined by polymerase chain reaction using buccal material. Axial and coronal intermediate- and T2-weighted MR images were quantified using a multispectral segmentation algorithm. Cognitive status was assessed by means of a modified Mini-Mental Status Examination.
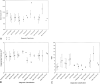
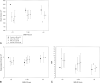
Results: All types of dementing illness showed significant volume reductions in the majority of structures examined, particularly in the total brain, hippocampus, and white and gray matter, and increased CSF and ventricular volumes. Subjects with mild cognitive impairment showed fewer atrophic changes but were still distinguishable from the 24 control subjects. Presence of an epsilon4 allele was associated with smaller hippocampal volume in subjects with Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia within just 1 year of disease onset. For other analyses, atrophy related to the presence of the epsilon4 allele disappeared after controlling for age and length of disease.
Conclusion: The effects of the epsilon4 allele on brain morphology may be subtly expressed early in the development of dementia, but do not specifically affect cerebral atrophy thereafter. Cognitive impairment is associated with atrophy irrespective of diagnosis and presence of epsilon4.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inheritance of the ApoE epsilon4 allele increases the rate of brain atrophy in dementia patients.Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 1999 Jul-Aug;10(4):262-8. doi: 10.1159/000017130. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 1999. PMID: 10364643 Clinical Trial.
-
Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele, temporal lobe atrophy, and white matter lesions in late-life dementias.Arch Neurol. 1999 Aug;56(8):961-5. doi: 10.1001/archneur.56.8.961. Arch Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10448801
-
Cognition, brain atrophy, and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers changes from preclinical to dementia stage of Alzheimer's disease and the influence of apolipoprotein e.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;45(1):253-68. doi: 10.3233/JAD-142451. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 25524955
-
Hippocampal atrophy and apolipoprotein E genotype are independently associated with Alzheimer's disease.Ann Neurol. 1998 Mar;43(3):303-10. doi: 10.1002/ana.410430307. Ann Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9506546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural magnetic resonance imaging for the early diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease in people with mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 2;3(3):CD009628. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009628.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32119112 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Impact of APOE on the healthy aging brain: a voxel-based MRI and DTI study.J Alzheimers Dis. 2009;18(3):553-64. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2009-1163. J Alzheimers Dis. 2009. PMID: 19584447 Free PMC article.
-
MRI Clinical Ratings and Cognitive Function in a Cross-Sectional Population Study of Dementia: The Cache County Memory Study.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2019;6(2):100-107. doi: 10.14283/jpad.2019.1. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 30756116 Free PMC article.
-
Transient ischaemic attacks are associated with increased rates of global cerebral atrophy.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003 Feb;74(2):213-6. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.74.2.213. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003. PMID: 12531953 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E genotype is associated with temporal and hippocampal atrophy rates in healthy elderly adults: a tensor-based morphometry study.J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;23(3):433-42. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-101398. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011. PMID: 21098974 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge-based localization of hippocampus in human brain MRI.Comput Biol Med. 2007 Sep;37(9):1342-60. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2006.12.010. Epub 2007 Mar 6. Comput Biol Med. 2007. PMID: 17339035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cummings JL, Vinters HV, Cole GM, Khachaturian ZS. Alzheimer's disease: etiologies, pathophysiology, cognitive reserve, and treatment opportunities. Neurology 1998;51:S2-S17 - PubMed
-
- Jorm AF, Jolley D. The incidence of dementia: a meta-analysis. Neurology 1998;51:728-733 - PubMed
-
- Mayeux R, Saunders AM, Shea S, et al. Utility of the apolipoprotein E genotype in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med 1998;338:506-511 - PubMed
-
- Kidron D, Black SE, Stanchev P, et al. Quantitative MR volumetry in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 1997;49:1504-1512 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
