Identification of ligands and coligands for the ecdysone-regulated gene switch
- PMID: 11114195
- PMCID: PMC18950
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.260499497
Identification of ligands and coligands for the ecdysone-regulated gene switch
Abstract
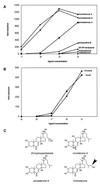
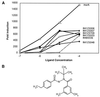
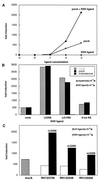
The ecdysone-inducible gene switch is a useful tool for modulating gene expression in mammalian cells and transgenic animals. We have identified inducers derived from plants as well as certain classes of insecticides that increase the versatility of this gene regulation system. Phytoecdysteroids share the favorable kinetics of steroids, but are inert in mammals. The gene regulation properties of one of these ecdysteroids have been examined in cell culture and in newly developed strains of ecdysone-system transgenic mice. Ponasterone A is a potent regulator of gene expression in cells and transgenic animals, enabling reporter genes to be turned on and off rapidly. A number of nonsteroidal insecticides have been identified that also activate the ecdysone system. Because the gene-controlling properties of the ecdysone switch are based on a heterodimer composed of a modified ecdysone receptor (VgEcR) and the retinoid X receptor (RXR), we have tested the effect of RXR ligands on the VgEcR/RXR complex. Used alone, RXR ligands display no activity on the ecdysone switch. However, when used in combination with a VgEcR ligand, RXR ligands dramatically enhance the absolute levels of induction. This property of the heterodimer has allowed the development of superinducer combinations that increase the dynamic range of the system.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

