Phosphorylation of histone H3 correlates with transcriptionally active loci
- PMID: 11114889
- PMCID: PMC317109
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.848800
Phosphorylation of histone H3 correlates with transcriptionally active loci
Abstract
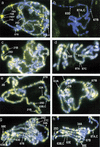
Posttranslational modifications of the N-terminal tails of the core histones within the nucleosome particle are thought to act as signals from the chromatin to the cell for various processes. The experiments presented here show that the acetylation of histones H3 and H4 in polytene chromosomes does not change during heat shock. In contrast, the global level of phosphorylated H3 decreased dramatically during a heat shock, with an observed increase in H3 phosphorylation at the heat shock loci. Additional experiments confirm that this change in phosphorylated H3 distribution is dependent on functional heat shock transcription factor activity. These experiments suggest that H3 phosphorylation has an important role in the induction of transcription during the heat shock response.
Figures
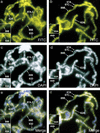
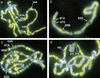
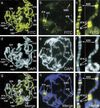
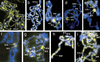

References
-
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. V. Responses to environmental treatments. Chromosoma. 1970;31:356–376. - PubMed
-
- ————— Puffing patterns in Drosophila melanogaster and related species. Results Probl Cell Differ. 1972;4:101–151. - PubMed
-
- ————— . Drosophila. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1989.
-
- Ashburner M, Bonner JJ. The induction of gene activity in Drosophila by heat shock. Cell. 1979;17:241–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
