Role of Bak in UV-induced apoptosis in skin cancer and abrogation by HPV E6 proteins
- PMID: 11114894
- PMCID: PMC317098
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.182100
Role of Bak in UV-induced apoptosis in skin cancer and abrogation by HPV E6 proteins
Abstract
Ultraviolet B (UVB) damage is recognized as the most important etiological factor in the development of skin cancer. Human papillomaviruses (HPV) have also been implicated in the disease, although the mechanism of action of these viruses remains unknown. We present evidence here that Bak protein is involved in signaling apoptosis in the skin in response to UVB damage, and that cutaneous HPV E6 proteins target and abrogate Bak function by promoting its proteolytic degradation both in vitro and in regenerated epithelium. Additionally, HPV positive skin cancers had undetectable levels of Bak in contrast to HPV negative cancers, which expressed Bak. This study supports a link between the virus and UVB in the induction of HPV-associated skin cancer and reveals a survival mechanism of virally infected cells.
Figures




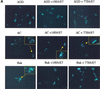

References
-
- Burger H, Hooter K, Boersma AWM, Kortland CJ, Van Den Berg AP, Stoter G. Expression of p53, p21Waf/Cip, Bcl-2, Bax, Bcl-X and Bak in radiation-induced apoptosis in testicular germ cell tumour lines. Int J Radiation Oncology Biol Phys. 1998;41:415–424. - PubMed
-
- Craiu A, Gaczynska M, Akopian T, Gramm CF, Fenteany G, Goldberg AL, Rock KL. Lactacystin and clasto-lactacystin β-lactone modify multiple proteosome β-subunits and inhibit intracellular protein degradation and major histocompatibility complex class I antigen presentation. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:13437–13445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
