Targeted random mutagenesis to identify functionally important residues in the D2 protein of photosystem II in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803
- PMID: 11114911
- PMCID: PMC94860
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.1.145-154.2001
Targeted random mutagenesis to identify functionally important residues in the D2 protein of photosystem II in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803
Abstract
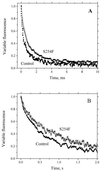
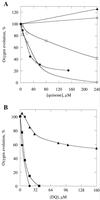
To identify important residues in the D2 protein of photosystem II (PSII) in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803, we randomly mutagenized a region of psbDI (coding for a 96-residue-long C-terminal part of D2) with sodium bisulfite. Mutagenized plasmids were introduced into a Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 mutant that lacks both psbD genes, and mutants with impaired PSII function were selected. Nine D2 residues were identified that are important for PSII stability and/or function, as their mutation led to impairment of photoautotrophic growth. Five of these residues are likely to be involved in the formation of the Q(A)-binding niche; these are Ala249, Ser254, Gly258, Ala260, and His268. Three others (Gly278, Ser283, and Gly288) are in transmembrane alpha-helix E, and their alteration leads to destabilization of PSII but not to major functional alterations of the remaining centers, indicating that they are unlikely to interact directly with cofactors. In the C-terminal lumenal tail of D2, only one residue (Arg294) was identified as functionally important for PSII. However, from the number of mutants generated it is likely that most or all of the 70 residues that are susceptible to bisulfite mutagenesis have been altered at least once. The fact that mutations in most of these residues have not been picked up by our screening method suggests that these mutations led to a normal photoautotrophic phenotype. A novel method of intragenic complementation in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 was developed to facilitate genetic analysis of psbDI mutants containing several amino acid changes in the targeted domain. Recombination between genome copies in the same cell appears to be much more prevalent in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 than was generally assumed.
Figures


References
-
- Cao J, Vermaas W F J, Govindjee Arginine residues in the D2 polypeptide may stabilize bicarbonate binding in photosystem II of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1059:171–180. - PubMed
-
- Chang C-H, Tiede D, Tang J, Smith U, Norris J. Structure of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides R-26 reaction center. FEBS Lett. 1986;205:82–86. - PubMed
-
- Chu H-A, Nguyen A P, Debus R J. Amino acid residues that influence the binding of manganese or calcium to photosystem II. 2. The carboxy-terminal domain of the D1 polypeptide. Biochemistry. 1994;34:5859–5882. - PubMed
-
- Deisenhofer J, Epp O, Miki K, Huber R, Michel H. Structure of the protein subunits in the photosynthetic reaction center of Rhodopseudomonas viridis at 3 Å resolution. Nature. 1985;318:618–624. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

