Renaturation of Bacillus thermoglucosidasius HrcA repressor by DNA and thermostability of the HrcA-DNA complex in vitro
- PMID: 11114912
- PMCID: PMC94861
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.1.155-161.2001
Renaturation of Bacillus thermoglucosidasius HrcA repressor by DNA and thermostability of the HrcA-DNA complex in vitro
Abstract
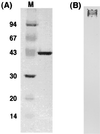
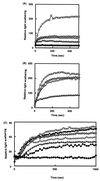
HrcA, a negative control repressor for chaperone expression from the obligate thermophile Bacillus thermoglucosidasius KP1006, was purified in a His-tagged form in the presence of 6 M urea but hardly renatured to an intact state due to extreme insolubility. Renaturation trials revealed that the addition of DNA to purified B. thermoglucosidasius HrcA can result in solubilization of HrcA free from the denaturing agent urea. Results from band shift and light scattering assays provided three new findings: (i) any species of DNA can serve to solubilize B. thermoglucosidasius HrcA, but DNA containing the CIRCE (controlling inverted repeat of chaperone expression) element is far more effective than other nonspecific DNA; (ii) B. thermoglucosidasius HrcA renatured with nonspecific DNA bound the CIRCE element in the molecular ratio of 2.6:1; and (iii) B. thermoglucosidasius HrcA binding to the CIRCE element was stable at below 50 degrees C whereas the complex was rapidly denatured at 70 degrees C, suggesting that the breakdown of HrcA is induced by heat stress and HrcA may act as a thermosensor to affect the expression of heat shock regulatory genes. These results will help to determine the nature of HrcA protein molecules.
Figures
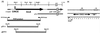
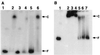
Similar articles
-
Identification of a helix-turn-helix motif of Bacillus thermoglucosidasius HrcA essential for binding to the CIRCE element and thermostability of the HrcA-CIRCE complex, indicating a role as a thermosensor.J Bacteriol. 2003 Jan;185(1):381-5. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.1.381-385.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12486078 Free PMC article.
-
The GroE chaperonin machine is a major modulator of the CIRCE heat shock regulon of Bacillus subtilis.EMBO J. 1997 Aug 1;16(15):4579-90. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.15.4579. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9303302 Free PMC article.
-
Stress response gene regulation in Chlamydia is dependent on HrcA-CIRCE interactions.J Bacteriol. 2004 Jun;186(11):3384-91. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.11.3384-3391.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15150223 Free PMC article.
-
Negative regulation of the heat shock response in Streptomyces.Arch Microbiol. 2001 Oct;176(4):237-42. doi: 10.1007/s002030100321. Arch Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11685367 Review.
-
Negative regulation of bacterial heat shock genes.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Jan;31(1):1-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01166.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 9987104 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a helix-turn-helix motif of Bacillus thermoglucosidasius HrcA essential for binding to the CIRCE element and thermostability of the HrcA-CIRCE complex, indicating a role as a thermosensor.J Bacteriol. 2003 Jan;185(1):381-5. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.1.381-385.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12486078 Free PMC article.
-
ClpL is required for folding of CtsR in Streptococcus mutans.J Bacteriol. 2013 Feb;195(3):576-84. doi: 10.1128/JB.01743-12. Epub 2012 Nov 30. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23204456 Free PMC article.
-
Feeling the Heat: The Campylobacter jejuni HrcA Transcriptional Repressor Is an Intrinsic Protein Thermosensor.Biomolecules. 2021 Sep 27;11(10):1413. doi: 10.3390/biom11101413. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34680046 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of the heat shock regulator HrcA of Chlamydia trachomatis.J Bacteriol. 2002 Dec;184(23):6566-71. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.23.6566-6571.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12426345 Free PMC article.
-
Chlamydial GroEL autoregulates its own expression through direct interactions with the HrcA repressor protein.J Bacteriol. 2005 Nov;187(21):7535-42. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.21.7535-7542.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 16237037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad S, Selvapandiyan A, Bhantnagar R K. A protein-based phylogenetic tree for gram-positive bacteria derived from hrcA, a unique heat-shock regulatory gene. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1999;49:1387–1394. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons; 1989.
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Dorman C J, Hinton J C, Free A. Domain organization and oligomerization among H-NS-like nucleoid-associated proteins in bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 1999;7:124–128. - PubMed
-
- Egan S M, Schleif R F. DNA-dependent renaturation of an insoluble DNA binding protein. Identification of the RhaA binding site at rhaBAD. J Mol Biol. 1994;243:821–829. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

