X-ray spectroscopy-based structure of the Mn cluster and mechanism of photosynthetic oxygen evolution
- PMID: 11115621
- PMCID: PMC3950273
- DOI: 10.1016/s0005-2728(00)00217-6
X-ray spectroscopy-based structure of the Mn cluster and mechanism of photosynthetic oxygen evolution
Abstract
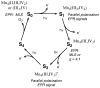
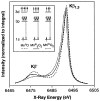
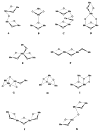
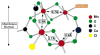
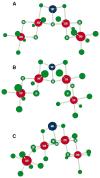
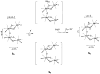
The mechanism by which the Mn-containing oxygen evolving complex (OEC) produces oxygen from water has been of great interest for over 40 years. This review focuses on how X-ray spectroscopy has provided important information about the structure of this Mn complex and its intermediates, or S-states, in the water oxidation cycle. X-ray absorption near-edge structure spectroscopy and high-resolution Mn Kbeta X-ray emission spectroscopy experiments have identified the oxidation states of the Mn in the OEC in each of the intermediate S-states, while extended X-ray absorption fine structure experiments have shown that 2.7 A Mn-Mn di-mu-oxo and 3.3 A Mn-Mn mono-mu-oxo motifs are present in the OEC. X-ray spectroscopy has also been used to probe the two essential cofactors in the OEC, Ca2+ and Cl-, and has shown that Ca2+ is an integral component of the OEC and is proximal to Mn. In addition, dichroism studies on oriented PS II membranes have provided angular information about the Mn-Mn and Mn-Ca vectors. Based on these X-ray spectroscopy data, refined models for the structure of the OEC and a mechanism for oxygen evolution by the OEC are presented.
Figures


References
-
- Debus RJ. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992;1102:269–352. - PubMed
-
- Babcock GT, Wikström M. Nature Lond. 1992;356:301–309. - PubMed
-
- Britt RD. In: Oxygenic Photosynthesis: The Light Reactions. Ort DR, Yocum CF, editors. Kluwer Academic; Dordrecht: 1996. pp. 137–164.
-
- Yachandra VK, Sauer K, Klein MP. Chem Rev. 1996;96:2927–2950. - PubMed
-
- Tommos C, Babcock GT. Acc Chem Res. 1998;31:18–25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

