Oral glutamine in the prevention of fluorouracil induced intestinal toxicity: a double blind, placebo controlled, randomised trial
- PMID: 11115819
- PMCID: PMC1728161
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.48.1.28
Oral glutamine in the prevention of fluorouracil induced intestinal toxicity: a double blind, placebo controlled, randomised trial
Abstract
Background: 5-Fluorouracil (FU) in association with folinic acid (FA) is the most frequently used chemotherapeutic agent in colorectal cancer but it often causes diarrhoea. Animal and human studies suggest that glutamine stimulates intestinal mucosal growth.
Aim: To determine if oral glutamine prevents changes in intestinal absorption (IA) and permeability (IP) induced by FU/FA.
Methods: Seventy chemotherapy naive patients with colorectal cancer were randomly assigned to oral glutamine (18 g/day) or placebo before the first cycle of FU (450 mg/m(2)) and FA (100 mg/m(2)) administered intravenously for five days. Treatment was continued for 15 days, starting five days before the beginning of chemotherapy. IA (D-xylose urinary excretion) and IP (cellobiose-mannitol test) were assessed at baseline and four and five days after the end of the first cycle of chemotherapy, respectively. Patients kept a daily record of diarrhoea, scored using the classification system of the National Cancer Institute (Bethesda, Maryland, USA). Duration of diarrhoea was recorded and the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated for each patient.
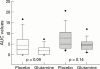
Results: Baseline patient characteristics and basal values of IP and IA tests were similar in the two arms. After one cycle of chemotherapy, the reduction in IA (D-xylose absorption) was more marked in the placebo arm (7.1% v 3. 8%; p=0.02); reduction of IP to mannitol was higher in the placebo arm (9.2% v 4.5%; p=0.02); and urinary recovery of cellobiose was not different between the study arms (p=0.60). Accordingly, the cellobiose-mannitol ratio increased more in the placebo arm (0.037 v 0.012; p=0.04). Average AUC of diarrhoea (1.9 v 4.5; p=0.09) and average number of loperamide tablets taken (0.4 v 2.6; p=0.002) were reduced in the glutamine arm.
Conclusions: Glutamine reduces changes in IA and IP induced by FU and may have a protective effect on FU induced diarrhoea.
Figures

Comment in
-
Intestinal permeability: the cellobiose/mannitol test.Gut. 2001 Aug;49(2):312. doi: 10.1136/gut.49.2.312. Gut. 2001. PMID: 11476080 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The effect of oral glutamine on 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin-induced mucositis/stomatitis assessed by intestinal permeability test.Clin Nutr. 2007 Feb;26(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2006.07.003. Epub 2006 Sep 1. Clin Nutr. 2007. PMID: 16949180 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil on intestinal permeability and absorption in patients with advanced colorectal cancer.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001 Mar;32(3):228-30. doi: 10.1097/00004836-200103000-00010. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11246350
-
Oral glutamine supplementation during preoperative radiochemotherapy in patients with rectal cancer: a randomised double blinded, placebo controlled pilot study.Clin Nutr. 2011 Oct;30(5):567-70. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2011.06.003. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Clin Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21733605 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase III controlled evaluation of glutamine for decreasing stomatitis in patients receiving fluorouracil (5-FU)-based chemotherapy.Am J Clin Oncol. 1999 Jun;22(3):258-61. doi: 10.1097/00000421-199906000-00009. Am J Clin Oncol. 1999. PMID: 10362332 Clinical Trial.
-
[Combination of 5-Fluorouracil and folinic acid--is it still the standard therapy for advanced colorectal carcinoma?].Tumori. 2000 Sep-Oct;86(5 Suppl 2):S19-25. Tumori. 2000. PMID: 11195298 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
A Randomized Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Role and Efficacy of Oral Glutamine in the Treatment of Chemo-radiotherapy-induced Oral Mucositis and Dysphagia in Patients with Oropharynx and Larynx Carcinoma.Cureus. 2019 Jun 7;11(6):e4855. doi: 10.7759/cureus.4855. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31410338 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of glutamine on intestinal injury and bacterial community in rats exposed to hypobaric hypoxia environment.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Apr 28;20(16):4662-74. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4662. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24782618 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of glutamine intake on complications of colorectal and colon cancer treatment: A systematic review.J Res Med Sci. 2015 Sep;20(9):910-8. doi: 10.4103/1735-1995.170634. J Res Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26759580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic review of agents for the management of gastrointestinal mucositis in cancer patients.Support Care Cancer. 2013 Jan;21(1):313-26. doi: 10.1007/s00520-012-1644-z. Epub 2012 Nov 10. Support Care Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23142924
-
Alanyl-glutamine and glutamine supplementation improves 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal epithelium damage in vitro.Dig Dis Sci. 2008 Oct;53(10):2687-96. doi: 10.1007/s10620-008-0215-0. Epub 2008 Mar 6. Dig Dis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18320312 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
