The Arabidopsis genome. An abundance of soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor adaptor protein receptors
- PMID: 11115874
- PMCID: PMC59855
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.124.4.1558
The Arabidopsis genome. An abundance of soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor adaptor protein receptors
Abstract
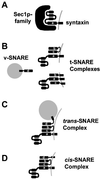
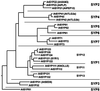
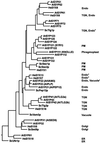
Many factors have been characterized as essential for vesicle trafficking, including a number of proteins commonly referred to as soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor adaptor protein receptor (SNARE) components. The Arabidopsis genome contains a remarkable number of SNAREs. In general, the vesicle fusion machinery appears highly conserved. However, whereas some classes of yeast and mammalian genes appear to be lacking in Arabidopsis, this small plant genome has gene families not found in other eukaryotes. Very little is known about the precise function of plant SNAREs. By contrast, the intracellular localization of and interactions between a large number of plant SNAREs have been determined, and these data are discussed in light of the phylogenetic analysis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Systematic analysis of SNARE molecules in Arabidopsis: dissection of the post-Golgi network in plant cells.Cell Struct Funct. 2004 Apr;29(2):49-65. doi: 10.1247/csf.29.49. Cell Struct Funct. 2004. PMID: 15342965
-
A new catch in the SNARE.Trends Plant Sci. 2004 Apr;9(4):187-95. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.02.007. Trends Plant Sci. 2004. PMID: 15063869 Review.
-
The SNARE protein family of Leishmania major.BMC Genomics. 2006 Oct 6;7:250. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-250. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 17026746 Free PMC article.
-
NPSN11 is a cell plate-associated SNARE protein that interacts with the syntaxin KNOLLE.Plant Physiol. 2002 Jun;129(2):530-9. doi: 10.1104/pp.003970. Plant Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12068098 Free PMC article.
-
SNAREs and membrane fusion in the Golgi apparatus.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Aug 14;1404(1-2):9-31. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(98)00044-5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9714710 Review.
Cited by
-
The SNARE protein SYP71 expressed in vascular tissues is involved in symbiotic nitrogen fixation in Lotus japonicus nodules.Plant Physiol. 2012 Oct;160(2):897-905. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.200782. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22858633 Free PMC article.
-
Toward understanding vesicle traffic and the guard cell model.New Phytol. 2002 Mar;153(3):405-413. doi: 10.1046/j.0028-646X.2001.00341.x. Epub 2002 Mar 5. New Phytol. 2002. PMID: 33863212 Review.
-
FcLDP1, a Gene Encoding a Late Embryogenesis Abundant (LEA) Domain Protein, Responds to Brassinosteroids and Abscisic Acid during the Development of Fruits in Fragaria chiloensis.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Jun 14;7:788. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00788. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27379111 Free PMC article.
-
The citrus fruit proteome: insights into citrus fruit metabolism.Planta. 2007 Sep;226(4):989-1005. doi: 10.1007/s00425-007-0545-8. Epub 2007 May 31. Planta. 2007. PMID: 17541628
-
R-SNARE homolog MoSec22 is required for conidiogenesis, cell wall integrity, and pathogenesis of Magnaporthe oryzae.PLoS One. 2010 Oct 6;5(10):e13193. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013193. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20949084 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aalto MK, Ruohonen L, Hosono K, Keranen S. Cloning and sequencing of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae SEC1 gene localized on chromosome IV. Yeast. 1991;7:643–650. - PubMed
-
- Abeliovich H, Grote E, Novick P, Ferro-Novick S. Tlg2p, a yeast syntaxin homolog that resides on the Golgi and endocytic structures. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:11719–11727. - PubMed
-
- Adams MD. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 2000;287:2185–2195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

