Arabidopsis mutants resistant to S(+)-beta-methyl-alpha, beta-diaminopropionic acid, a cycad-derived glutamate receptor agonist
- PMID: 11115879
- PMCID: PMC59860
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.124.4.1615
Arabidopsis mutants resistant to S(+)-beta-methyl-alpha, beta-diaminopropionic acid, a cycad-derived glutamate receptor agonist
Abstract
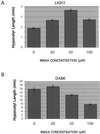
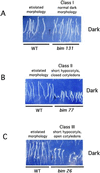
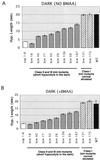
Ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs) are ligand-gated ion channels that are the predominant neuroreceptors in the mammalian brain. Genes with high sequence similarity to animal iGluRs have been identified in Arabidopsis. To understand the role of Arabidopsis glutamate receptor-like (AtGLR) genes in plants, we have taken a pharmacological approach by examining the effects of BMAA [S(+)-beta-methyl-alpha, beta-diaminopropionic acid], a cycad-derived iGluR agonist, on Arabidopsis morphogenesis. When applied to Arabidopsis seedlings, BMAA caused a 2- to 3-fold increase in hypocotyl elongation and inhibited cotyledon opening during early seedling development. The effect of BMAA on hypocotyl elongation is light specific. Furthermore, BMAA effects on early morphogenesis of Arabidopsis can be reversed by the simultaneous application of glutamate, the native iGluR agonist in animals. To determine the targets of BMAA action in Arabidopsis, a genetic screen was devised to isolate Arabidopsis mutants with a BMAA insensitive morphology (bim). When grown in the light on BMAA, bim mutants exhibited short hypocotyls compared with wild type. bim mutants were grouped into three classes based on their morphology when grown in the dark in the absence of BMAA. Class-I bim mutants have a normal, etiolated morphology, similar to wild-type plants. Class-II bim mutants have shorter hypocotyls and closed cotyledons when grown in the dark. Class-III bim mutants have short hypocotyls and open cotyledons when grown in the dark, resembling the previously characterized constitutively photomorphogenic mutants (cop, det, fus, and shy). Further analysis of the bim mutants should help define whether plant-derived iGluR agonists target glutamate receptor signaling pathways in plants.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A mutation in the Proteosomal Regulatory Particle AAA-ATPase-3 in Arabidopsis impairs the light-specific hypocotyl elongation response elicited by a glutamate receptor agonist, BMAA.Plant Mol Biol. 2009 Jul;70(5):523-33. doi: 10.1007/s11103-009-9489-7. Epub 2009 May 2. Plant Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19412571
-
Jasmonate inhibits COP1 activity to suppress hypocotyl elongation and promote cotyledon opening in etiolated Arabidopsis seedlings.Plant J. 2017 Jun;90(6):1144-1155. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13539. Epub 2017 Apr 29. Plant J. 2017. PMID: 28321936
-
Involvement of COP1 in ethylene- and light-regulated hypocotyl elongation.Planta. 2012 Dec;236(6):1791-802. doi: 10.1007/s00425-012-1730-y. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Planta. 2012. PMID: 22890836
-
The COP/DET/FUS proteins-regulators of eukaryotic growth and development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2000 Dec;11(6):495-503. doi: 10.1006/scdb.2000.0203. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2000. PMID: 11145879 Review.
-
Glutamate receptor-like channels in plants: a role as amino acid sensors in plant defence?F1000Prime Rep. 2014 Jun 2;6:37. doi: 10.12703/P6-37. eCollection 2014. F1000Prime Rep. 2014. PMID: 24991414 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systems approach identifies an organic nitrogen-responsive gene network that is regulated by the master clock control gene CCA1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Mar 25;105(12):4939-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0800211105. Epub 2008 Mar 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18344319 Free PMC article.
-
Acute β-N-Methylamino-L-alanine Toxicity in a Mouse Model.J Toxicol. 2015;2015:739746. doi: 10.1155/2015/739746. Epub 2015 Oct 29. J Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 26604922 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate receptors in plants.Ann Bot. 2002 Nov;90(5):549-57. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcf228. Ann Bot. 2002. PMID: 12466095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The putative glutamate receptor 1.1 (AtGLR1.1) functions as a regulator of carbon and nitrogen metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 May 27;100(11):6872-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1030961100. Epub 2003 May 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12738881 Free PMC article.
-
Merging Signaling with Structure: Functions and Mechanisms of Plant Glutamate Receptor Ion Channels.Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2023 May 22;74:415-452. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-070522-033255. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 36854472 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad M, Cashmore AR. The HY4 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana encodes a protein with characteristics of a blue light photoreceptor. Nature. 1993;366:162–166. - PubMed
-
- Bettler B, Mulle C. Review: neurotransmitter receptors II AMPA and kainate receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1995;34:123–139. - PubMed
-
- Chamberlain CJ. The living cycads. In: Moore EH, Coulter JM, Millikan RA, editors. The University of Chicago Science Series. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press; 1919. , p ix.
-
- Chen G-Q, Cui C, Mayer ML, Gouaux E. Functional characterization of a potassium-selective prokaryotic glutamate receptor. Nature. 1999;402:817–821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

