Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) by their ligands and protein kinase A activators
- PMID: 11117527
- PMCID: PMC2040490
- DOI: 10.1210/mend.14.12.0575
Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) by their ligands and protein kinase A activators
Abstract
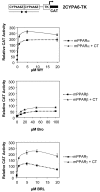
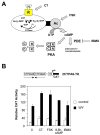
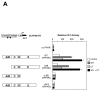
The nuclear peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) alpha, beta, and gamma activate the transcription of multiple genes involved in lipid metabolism. Several natural and synthetic ligands have been identified for each PPAR isotype but little is known about the phosphorylation state of these receptors. We show here that activators of protein kinase A (PKA) can enhance mouse PPAR activity in the absence and the presence of exogenous ligands in transient transfection experiments. Activation function 1 (AF-1) of PPARs was dispensable for transcriptional enhancement, whereas activation function 2 (AF-2) was required for this effect. We also show that several domains of PPAR can be phosphorylated by PKA in vitro. Moreover, gel retardation experiments suggest that PKA stabilizes binding of the liganded PPAR to DNA. PKA inhibitors decreased not only the kinase-dependent induction of PPARs but also their ligand-dependent induction, suggesting an interaction between both pathways that leads to maximal transcriptional induction by PPARs. Moreover, comparing PPAR alpha knockout (KO) with PPAR alpha WT mice, we show that the expression of the acyl CoA oxidase (ACO) gene can be regulated by PKA-activated PPAR alpha in liver. These data demonstrate that the PKA pathway is an important modulator of PPAR activity, and we propose a model associating this pathway in the control of fatty acid beta-oxidation under conditions of fasting, stress, and exercise.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Functional interactions of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor, retinoid-X receptor, and Sp1 in the transcriptional regulation of the acyl-coenzyme-A oxidase promoter.Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Feb;9(2):219-31. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.2.7776972. Mol Endocrinol. 1995. PMID: 7776972
-
Conserved amino acids in the ligand-binding and tau(i) domains of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha are necessary for heterodimerization with RXR.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1999 Jan 25;147(1-2):37-47. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(98)00217-2. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1999. PMID: 10195690
-
Regulation of energy metabolism by long-chain fatty acids.Prog Lipid Res. 2014 Jan;53:124-44. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Prog Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24362249 Review.
-
Addition of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha to guinea pig hepatocytes confers increased responsiveness to peroxisome proliferators.Cancer Res. 1999 Oct 1;59(19):4776-80. Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10519382
-
Peroxisome proliferators and peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPARs) as regulators of lipid metabolism.Biochimie. 1997 Feb-Mar;79(2-3):81-94. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(97)81496-4. Biochimie. 1997. PMID: 9209701 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term effects of acute low-dose ionizing radiation on the neonatal mouse heart: a proteomic study.Radiat Environ Biophys. 2013 Nov;52(4):451-61. doi: 10.1007/s00411-013-0483-8. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2013. PMID: 23880982
-
The Potential Role of PPARs in the Fetal Origins of Adult Disease.Cells. 2022 Nov 2;11(21):3474. doi: 10.3390/cells11213474. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PPARgamma and PPARdelta negatively regulate specific subsets of lipopolysaccharide and IFN-gamma target genes in macrophages.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 May 27;100(11):6712-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1031789100. Epub 2003 May 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12740443 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the Beneficial Role of PPAR Agonists in Cardiac Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 4;19(11):3464. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113464. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30400386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiopoietin-like protein 4 is an exercise-induced hepatokine in humans, regulated by glucagon and cAMP.Mol Metab. 2017 Oct;6(10):1286-1295. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.06.018. Epub 2017 Jul 8. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 29031727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- A unified nomenclature system for the nuclear receptor superfamily. Cell. 1999;97:161–3. [letter] - PubMed
-
- Desvergne B, Wahli W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:649–88. - PubMed
-
- Beato M, Herrlich P, Schutz G. Steroid hormone receptors: many actors in search of a plot. Cell. 1995;83:851–7. - PubMed
-
- Issemann I, Green S. Activation of a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature. 1990;347:645–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

