In vivo kinetics of protein targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum determined by site-specific phosphorylation
- PMID: 11118205
- PMCID: PMC366643
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.24.6704
In vivo kinetics of protein targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum determined by site-specific phosphorylation
Abstract
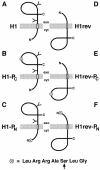
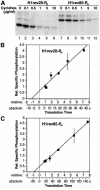
We have developed a novel assay to detect the cytosolic localization of protein domains by inserting a short consensus sequence for phosphorylation by protein kinase A. In transfected COS-1 cells, this sequence was labeled efficiently with [(32)P]phosphate only when exposed to the cytosol and not when translocated into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. The phosphorylation state of this sequence can therefore be used to determine the topology of membrane proteins. This assay is sufficiently sensitive to detect even the transient cytosolic exposure of the N-terminal domain of a membrane protein with a reverse signal-anchor sequence. The extent of phosphorylation per newly synthesized polypeptide was shown to reflect the time of exposure to the cytosol, which depends on translation, targeting and translocation of the N-terminus. By altering the length of the N-terminal domain or manipulating the translation rate, it was determined that protein targeting is rapid and requires only a few seconds. The rate of N-terminal translocation was estimated to be approximately 1.6 times the rate of translation.
Figures



References
-
- Beltzer J.P., Fiedler,K., Fuhrer,C., Geffen,I., Handschin,C., Wessels,H.P. and Spiess,M. (1991) Charged residues are major determinants of the transmembrane orientation of a signal-anchor sequence. J. Biol. Chem., 266, 973–978. - PubMed
-
- Dale H. and Krebs,M.P. (1999) Membrane insertion kinetics of a protein domain in vivo. The bacterioopsin N terminus inserts co-translationally. J. Biol. Chem., 274, 22693–22698. - PubMed
-
- Ellis L., Clauser,E., Morgan,D.O., Edery,M., Roth,R.A. and Rutter,W.J. (1986) Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell, 45, 721–732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

