Patterns of histone acetylation suggest dual pathways for gene activation by a bifunctional locus control region
- PMID: 11118216
- PMCID: PMC305892
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.24.6814
Patterns of histone acetylation suggest dual pathways for gene activation by a bifunctional locus control region
Abstract
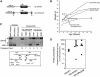
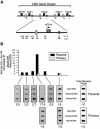
The five genes of the human growth hormone (hGH) cluster are expressed in either the pituitary or placenta. Activation of the cluster is dependent on a locus control region (LCR) comprising pituitary- specific (HSI,II, -15 kb), placenta-specific (HSIV, -30 kb) and shared (HSIII, -28 kb; HSV, -32 kb) DNase I hypersensitive sites. Gene activation in the pituitary is paralleled by acetylation of a 32 kb chromatin domain 5' to the cluster centered at HSI,II. In the present study we observed that acetylation of this region in placental chromatin was discretely limited to shared HSIII and HSV. Transgenic studies revealed placenta-specific activation of linked genes by a determinant (P-element) located 2 kb 5' to each of the four placentally expressed genes. A localized peak of histone acetylation was observed at these P-elements in placenta but not pituitary. These data support a model for bifunctional action of the hGH LCR in which separate positive determinants, HSI,II and the P-elements, activate their respective target genes by tissue-specific recruitment of distinctly regulated histone acetyl transferase activities.
Figures
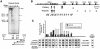

References
-
- Bennani-Baiti I.M., Jones,B.K., Liebhaber,S.A. and Cooke,N.E. (1995) Physical linkage of the human growth hormone gene cluster and the skeletal muscle sodium channel α-subunit gene (SCN4A) on chromosome 17. Genomics, 29, 647–652. - PubMed
-
- Bennani-Baiti I.M., Asa,S.L., Song,D., Iratni,R., Liebhaber,S.A. and Cooke,N.E. (1998a) DNase I-hypersensitive sites I and II of the human growth hormone locus control region are a major developmental activator of somatotrope gene expression. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 10655–10660. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bennani-Baiti I.M., Cooke,N.E. and Liebhaber,S.A. (1998b) Physical linkage of the human growth hormone gene cluster and the CD79b (Igβ/B29) gene. Genomics, 48, 258–264. - PubMed
-
- Brem G., Wanke,R., Wolf,E., Buchmuller,T., Muller,M., Brenig,B. and Hermanns,W. (1989) Multiple consequences of human growth hormone expression in transgenic mice. Mol. Biol. Med., 6, 531–547. - PubMed
-
- Brownell J.E. and Allis,C.D. (1996) Special HATs for special occasions: linking histone acetylation to chromatin assembly and gene activation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 6, 176–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

