Escherichia coli RNA polymerase core and holoenzyme structures
- PMID: 11118218
- PMCID: PMC305883
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.24.6833
Escherichia coli RNA polymerase core and holoenzyme structures
Abstract
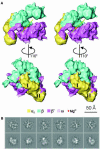
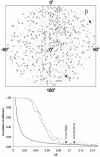
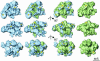
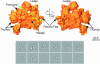
Multisubunit RNA polymerase is an essential enzyme for regulated gene expression. Here we report two Escherichia coli RNA polymerase structures: an 11.0 A structure of the core RNA polymerase and a 9.5 A structure of the sigma(70) holoenzyme. Both structures were obtained by cryo-electron microscopy and angular reconstitution. Core RNA polymerase exists in an open conformation. Extensive conformational changes occur between the core and the holoenzyme forms of the RNA polymerase, which are largely associated with movements in ss'. All common RNA polymerase subunits (alpha(2), ss, ss') could be localized in both structures, thus suggesting the position of sigma(70) in the holoenzyme.
Figures
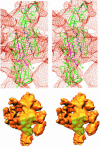
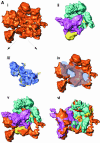

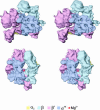
References
-
- Arthur T.M., Anthony,L.C. and Burgess,R.R. (2000) Mutational analysis of ‘β260–309’ a σ70 binding site located on E.coli core RNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 23113–23119. - PubMed
-
- Borukhov S. et al. (1991) Mapping of trypsin cleavage and antibody-binding sites and delineation of a dispensable domain in the β subunit of E.coli RNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem., 266, 23921–23926. - PubMed
-
- Burgess R. and Jendrisak,J. (1975) A procedure for the rapid, large scale purification of E.coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving polymin P precipitation and DNA–cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry, 14, 4634–4638. - PubMed
-
- Burgess R.R., Travers,A.A., Dunn,J.J. and Bautz,E.K.F. (1969) Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature, 221, 43–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

