GreA and GreB proteins revive backtracked RNA polymerase in vivo by promoting transcript trimming
- PMID: 11118220
- PMCID: PMC305891
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.24.6853
GreA and GreB proteins revive backtracked RNA polymerase in vivo by promoting transcript trimming
Abstract
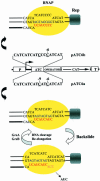
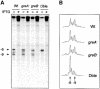
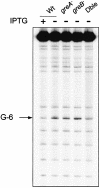
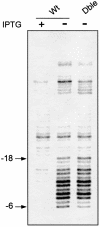
The GreA and GreB proteins of Escherichia coli show a multitude of effects on transcription elongation in vitro, yet their physiological functions are poorly understood. Here, we investigated whether and how these factors influence lateral oscillations of RNA polymerase (RNAP) in vivo, observed at a protein readblock. When RNAP is stalled within an (ATC/TAG)(n) sequence, it appears to oscillate between an upstream and a downstream position on the template, 3 bp apart, with concomitant trimming of the transcript 3' terminus and its re-synthesis. Using a set of mutant E.coli strains, we show that the presence of GreA or GreB in the cell is essential to induce this trimming. We show further that in contrast to a ternary complex that is stabilized at the downstream position, the oscillating complex relies heavily on the GreA/GreB-induced 'cleavage-and-restart' process to become catalytically competent. Clearly, by promoting transcript shortening and re-alignment of the catalytic register, the Gre factors function in vivo to rescue RNAP from being arrested at template positions where the lateral stability of the ternary complex is impaired.
Figures
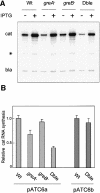
Similar articles
-
Effects of DksA, GreA, and GreB on transcription initiation: insights into the mechanisms of factors that bind in the secondary channel of RNA polymerase.J Mol Biol. 2007 Mar 2;366(4):1243-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.12.013. Epub 2006 Dec 12. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17207814 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic transcript cleavage activity of RNA polymerase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 9;92(10):4596-600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.10.4596. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7538676 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct functions of N and C-terminal domains of GreA, an Escherichia coli transcript cleavage factor.J Mol Biol. 1998 Feb 20;276(2):379-89. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.1545. J Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9512710
-
[The role of GreA and GreB factors in bacterial transcription elongation].Postepy Biochem. 2001;47(1):30-7. Postepy Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11503438 Review. Polish. No abstract available.
-
Conformational toggle triggers a modulator of RNA polymerase activity.Trends Biochem Sci. 2006 Aug;31(8):424-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.06.004. Epub 2006 Jul 11. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006. PMID: 16815708 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of genes involved in low aminoglycoside-induced SOS response in Vibrio cholerae: a role for transcription stalling and Mfd helicase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Feb;42(4):2366-79. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1259. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24319148 Free PMC article.
-
Highly tunable TetR-dependent target gene expression in the acetic acid bacterium Gluconobacter oxydans.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Sep;105(18):6835-6852. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11473-x. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34448898 Free PMC article.
-
Early transcriptional changes of heavy metal resistance and multiple efflux genes in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris under copper and heavy metal ion stress.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Mar 9;24(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03206-7. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38461228 Free PMC article.
-
Functions that protect Escherichia coli from DNA-protein crosslinks.DNA Repair (Amst). 2015 Apr;28:48-59. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.01.016. Epub 2015 Feb 7. DNA Repair (Amst). 2015. PMID: 25731940 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription-repair coupling factor Mfd associates with RNA polymerase in the absence of exogenous damage.Nat Commun. 2018 Apr 20;9(1):1570. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03790-z. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29679003 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

