Molecular basis of sequence-specific recognition of pre-ribosomal RNA by nucleolin
- PMID: 11118222
- PMCID: PMC305906
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.24.6870
Molecular basis of sequence-specific recognition of pre-ribosomal RNA by nucleolin
Abstract
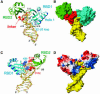
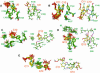
The structure of the 28 kDa complex of the first two RNA binding domains (RBDs) of nucleolin (RBD12) with an RNA stem-loop that includes the nucleolin recognition element UCCCGA in the loop was determined by NMR spectroscopy. The structure of nucleolin RBD12 with the nucleolin recognition element (NRE) reveals that the two RBDs bind on opposite sides of the RNA loop, forming a molecular clamp that brings the 5' and 3' ends of the recognition sequence close together and stabilizing the stem-loop. The specific interactions observed in the structure explain the sequence specificity for the NRE sequence. Binding studies of mutant proteins and analysis of conserved residues support the proposed interactions. The mode of interaction of the protein with the RNA and the location of the putative NRE sites suggest that nucleolin may function as an RNA chaperone to prevent improper folding of the nascent pre-rRNA.
Figures





References
-
- Allain F.H.-T., Gubser,C.C., Howe,P.W.A., Nagai,K. Neuhaus,D. and Varani,G. (1996) Specificity of ribonucleoprotein interaction determined by RNA folding during complex formulation. Nature, 380, 646–650. - PubMed
-
- Allain F.H.-T., Gilbert,D.E., Bouvet,P. and Feigon,J. (2000) Solution structure of the two N-terminal RNA-binding domains of Nucleolin and NMR study of the interaction with its RNA target. J. Mol. Biol., 303, 227–241. - PubMed
-
- Bartels C., Xia,T.H., Billeter,M., Guntert,P. and Wuthrich,K. (1995) The program Xeasy for computer-supported NMR spectral analysis of biological macromolecules. J. Biomol. NMR, 6, 1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

