Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli TibA glycoprotein adheres to human intestine epithelial cells
- PMID: 11119488
- PMCID: PMC97854
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.1.52-57.2001
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli TibA glycoprotein adheres to human intestine epithelial cells
Abstract
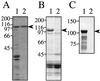
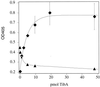
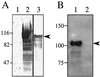
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) is capable of invading epithelial cell lines derived from the human ileum and colon. Two separate invasion loci (tia and tib) that direct noninvasive E. coli strains to adhere to and invade cultured human intestine epithelial cells have previously been isolated from the classical ETEC strain H10407. The tib locus directs the synthesis of TibA, a 104-kDa outer membrane glycoprotein. Synthesis of TibA is directly correlated with the adherence and invasion phenotypes of the tib locus, suggesting that this protein is an adhesin and invasin. Here we report the purification of TibA and characterization of its biological activity. TibA was purified by continuous-elution preparative sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Purified TibA was biotin labeled and then shown to bind to HCT8 human ileocecal epithelial cells in a specific and saturable manner. Unlabeled TibA competed with biotin-labeled TibA, suggesting the presence of a specific TibA receptor in HCT8 cells. These results show that TibA acts as an adhesin. Polyclonal anti-TibA antiserum inhibited invasion of ETEC strain H10407 and of recombinant E. coli bearing tib locus clones, suggesting that TibA also acts as an invasin. The ability of TibA to direct epithelial cell adhesion suggests a role for this protein in ETEC pathogenesis.
Figures
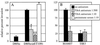
Similar articles
-
Epithelial cell adherence mediated by the enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli tia protein.Infect Immun. 2000 Dec;68(12):6595-601. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.12.6595-6601.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 11083770 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a glycoprotein produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 1999 Aug;67(8):4084-91. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.8.4084-4091.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10417177 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial cell invasion and adherence directed by the enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli tib locus is associated with a 104-kilodalton outer membrane protein.Infect Immun. 1994 Aug;62(8):3463-71. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.8.3463-3471.1994. Infect Immun. 1994. PMID: 8039917 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of the tia invasion locus from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 1996 Jun;64(6):2256-65. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.6.2256-2265.1996. Infect Immun. 1996. PMID: 8675335 Free PMC article.
-
Self-associating autotransporters, SAATs: functional and structural similarities.Int J Med Microbiol. 2006 Aug;296(4-5):187-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.10.002. Int J Med Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16600681 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional substitution of the TibC protein of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains for the autotransporter adhesin heptosyltransferase of the AIDA system.Infect Immun. 2002 May;70(5):2264-70. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.5.2264-2270.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 11953358 Free PMC article.
-
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: intestinal pathogenesis mechanisms and colonization resistance by gut microbiota.Gut Microbes. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2055943. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2055943. Gut Microbes. 2022. PMID: 35358002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.EcoSal Plus. 2016 Oct;7(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0006-2016. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0006-2016. EcoSal Plus. 2016. PMID: 27735786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of DNA microarrays to study the evolutionary genomics of Yersinia pestis and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis.Genome Res. 2003 Sep;13(9):2018-29. doi: 10.1101/gr.1507303. Genome Res. 2003. PMID: 12952873 Free PMC article.
-
Type V Secretion: the Autotransporter and Two-Partner Secretion Pathways.EcoSal Plus. 2010 Sep;4(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.4.3.6. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.4.3.6. EcoSal Plus. 2010. PMID: 26443787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benz I, Schmidt M A. AIDA-I, the adhesion involved in diffuse adherence of the diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli strain 2787 (O126:H27), is synthesized via a precursor molecule. Mol Microbiol. 1992;6:1539–1546. - PubMed
-
- Black R. Epidemiology of diarrhoeal disease: implications for control by vaccines. Vaccine. 1993;11:100–106. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Cassels F J, Wolf M K. Colonization factors of diarrheagenic E. coli and their intestinal receptors. J Ind Microbiol. 1995;15:214–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

