Role of plasma, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, and CD14 in response of mouse peritoneal exudate macrophages to endotoxin
- PMID: 11119527
- PMCID: PMC97893
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.1.378-385.2001
Role of plasma, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, and CD14 in response of mouse peritoneal exudate macrophages to endotoxin
Abstract
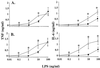
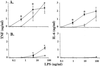
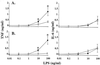
Plasma lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein (LBP) and membrane CD14 function to enhance the responses of monocytes to low concentrations of endotoxin. Surprisingly, recent reports have suggested that LBP or CD14 may be dispensable for macrophage responses to low concentrations of LPS or may even exert an inhibitory effect in the case of LBP. We therefore investigated whether LBP and CD14 participated in the response of mouse peritoneal exudate macrophages (PEM) to LPS stimulation. In the presence of a low amount of plasma (<1%) or of recombinant mouse or human LBP, PEM were found to respond to low concentrations of LPS (<5 to 10 ng/ml) in an LBP- and CD14-dependent manner. However, tumor necrosis factor production (not interleukin-6 production) by LPS-stimulated PEM was reduced when cells were stimulated in the presence of higher concentrations of plasma or serum (5 or 10%). Yet, the inhibitory effect of plasma or serum was not mediated by LBP. Taken together with previous results obtained with LBP and CD14 knockout mice in models of experimental endotoxemia, the present data confirm a critical part for LBP and CD14 in innate immune responses of both blood monocytes and tissue macrophages to endotoxins.
Figures



References
-
- Adachi Y, Satokawa C, Saeki M, Ohno N, Tamura H, Tanaka S, Yadomae T. Inhibition by a CD14 monoclonal antibody of lipopolysaccharide binding to murine macrophages. J Endotoxin Res. 1999;5:139–146.
-
- Amura C R, Chen L C, Hirohashi N, Lei M G, Morrison D C. Two functionally independent pathways for lipopolysaccharide-dependent activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1998;159:5079–5083. - PubMed
-
- Amura C R, Kamei T, Ito N, Soares M J, Morrison D C. Differential regulation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) activation pathways in mouse macrophages by LPS-binding proteins. J Immunol. 1998;161:2552–2560. - PubMed
-
- Chow J C, Young D W, Golenbock D T, Christ W J, Gusovsky F. Toll-like receptor-4 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:10689–10692. - PubMed
-
- Dean D F, Bochsler P N, Caroll R C, Olchowy F W, Neilsen N R, Slauson D O. Signaling pathways for tissue factor expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated bovine alveolar macrophages. Am J Vet Res. 1998;59:445–451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

