Targeted disruption of the Kvlqt1 gene causes deafness and gastric hyperplasia in mice
- PMID: 11120752
- PMCID: PMC387258
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI10897
Targeted disruption of the Kvlqt1 gene causes deafness and gastric hyperplasia in mice
Abstract
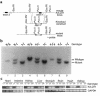
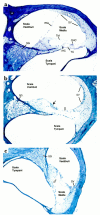
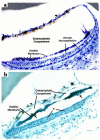
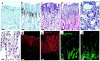
The KvLQT1 gene encodes a voltage-gated potassium channel. Mutations in KvLQT1 underlie the dominantly transmitted Ward-Romano long QT syndrome, which causes cardiac arrhythmia, and the recessively transmitted Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome, which causes both cardiac arrhythmia and congenital deafness. KvLQT1 is also disrupted by balanced germline chromosomal rearrangements in patients with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS), which causes prenatal overgrowth and cancer. Because of the diverse human disorders and organ systems affected by this gene, we developed an animal model by inactivating the murine Kvlqt1. No electrocardiographic abnormalities were observed. However, homozygous mice exhibited complete deafness, as well as circular movement and repetitive falling, suggesting imbalance. Histochemical study revealed severe anatomic disruption of the cochlear and vestibular end organs, suggesting that Kvlqt1 is essential for normal development of the inner ear. Surprisingly, homozygous mice also displayed threefold enlargement by weight of the stomach resulting from mucous neck cell hyperplasia. Finally, there were no features of BWS, suggesting that Kvlqt1 is not responsible for BWS.
Figures

Comment in
-
Antibodies against keratinocyte antigens other than desmogleins 1 and 3 can induce pemphigus vulgaris-like lesions.J Clin Invest. 2000 Dec;106(12):1467-79. doi: 10.1172/JCI10305. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 11120754 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
A novel mutation in the potassium channel gene KVLQT1 causes the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen cardioauditory syndrome.Nat Genet. 1997 Feb;15(2):186-9. doi: 10.1038/ng0297-186. Nat Genet. 1997. PMID: 9020846
-
Homozygous deletion in KVLQT1 associated with Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome.Circulation. 1999 Mar 16;99(10):1344-7. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.99.10.1344. Circulation. 1999. PMID: 10077519
-
Heterozygous mutation in the pore of potassium channel gene KvLQT1 causes an apparently normal phenotype in long QT syndrome.Eur J Hum Genet. 1998 Mar-Apr;6(2):129-33. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200165. Eur J Hum Genet. 1998. PMID: 9781056
-
KCNQ1 gene mutations and the respective genotype-phenotype correlations in the long QT syndrome.Med Sci Monit. 2002 Oct;8(10):RA240-8. Med Sci Monit. 2002. PMID: 12388934 Review.
-
[Clinical aspects and molecular genetics of the Jervell- and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome].Z Kardiol. 2002 May;91(5):380-8. doi: 10.1007/s00392-002-0789-z. Z Kardiol. 2002. PMID: 12132284 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Meta-analysis of the effect of KCNQ1 gene polymorphism on the risk of type 2 diabetes.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 May;40(5):3557-67. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2429-7. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23271129
-
Genetics of hearing and deafness.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2012 Nov;295(11):1812-29. doi: 10.1002/ar.22579. Epub 2012 Oct 8. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 23044516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aldosterone up-regulates voltage-gated potassium currents and NKCC1 protein membrane fractions.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 24;10(1):15604. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72450-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32973172 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models of long QT syndrome.J Physiol. 2007 Jan 1;578(Pt 1):43-53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.118745. Epub 2006 Oct 12. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17038432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abolition of Ca2+-mediated intestinal anion secretion and increased stool dehydration in mice lacking the intermediate conductance Ca2+-dependent K+ channel Kcnn4.J Physiol. 2007 Sep 1;583(Pt 2):705-17. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.134387. Epub 2007 Jun 21. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17584847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Q, et al. Positional cloning of a novel potassium channel gene: KVLQT1 mutations cause cardiac arrhythmias. Nat Genet. 1996;12:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Schulze-Bahr E, et al. KCNE1 mutations cause Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome. Nat Genet. 1997;17:267–268. - PubMed
-
- Splawski I, Tristani-Firouzi M, Lehmann MH, Sanguinetti MC, Keating MT. Mutations in the hminK gene cause long QT syndrome and suppress IKs function. Nat Genet. 1997;17:338–340. - PubMed
-
- Neyroud N, et al. A novel mutation in the potassium channel gene KvLQT1 causes the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen cardioauditory syndrome. Nat Genet. 1997;15:186–189. - PubMed
-
- Lee MP, Hu R-J, Johnson LA, Feinberg AP. Human KvLQT1 shows tissue-specific imprinting and is physically disrupted by Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome chromosomal rearrangements. Nat Genet. 1997;15:181–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

