TNF-alpha induces osteoclastogenesis by direct stimulation of macrophages exposed to permissive levels of RANK ligand
- PMID: 11120755
- PMCID: PMC387259
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI11176
TNF-alpha induces osteoclastogenesis by direct stimulation of macrophages exposed to permissive levels of RANK ligand
Abstract
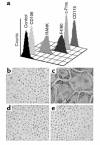
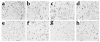
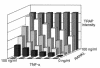
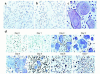
While TNF-alpha is pivotal to the pathogenesis of inflammatory osteolysis, the means by which it recruits osteoclasts and promotes bone destruction are unknown. We find that a pure population of murine osteoclast precursors fails to undergo osteoclastogenesis when treated with TNF-alpha alone. In contrast, the cytokine dramatically stimulates differentiation in macrophages primed by less than one percent of the amount of RANKL (ligand for the receptor activator of NF-kappaB) required to induce osteoclast formation. Mirroring their synergistic effects on osteoclast differentiation, TNF-alpha and RANKL markedly potentiate NF-kappaB and stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase activity, two signaling pathways essential for osteoclastogenesis. In vivo administration of TNF-alpha prompts robust osteoclast formation in chimeric animals in which ss-galactosidase positive, TNF-responsive macrophages develop within a TNF-nonresponsive stromal environment. Thus, while TNF-alpha alone does not induce osteoclastogenesis, it does so both in vitro and in vivo by directly targeting macrophages within a stromal environment that expresses permissive levels of RANKL. Given the minuscule amount of RANKL sufficient to synergize with TNF-alpha to promote osteoclastogenesis, TNF-alpha appears to be a more convenient target in arresting inflammatory osteolysis.
Figures




References
-
- Lannigan FJ, O’Higgins P, McPhie P. The cellular mechanism of ossicular erosion in chronic suppurative otitis media. J Laryngol Otol. 1993;107:12–16. - PubMed
-
- Baroukh B, Saffar JL. Identification of osteoclasts and their mononuclear precursors. A comparative histological and histochemical study in hamster periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 1991;26:161–166. - PubMed
-
- Bom-van Noorloos AA, et al. Bacteroides gingivalis stimulates bone resorption via interleukin-1 production by mononuclear cells. J Clin Periodontol. 1990;17:409–413. - PubMed
-
- Birkedal-Hansen H. Role of cytokines and inflammatory mediators in tissue destruction. J Periodontal Res. 1993;28:500–510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

