Kinetic study of the inflammatory response in Streptococcus pneumoniae experimental pneumonia treated with the ketolide HMR 3004
- PMID: 11120974
- PMCID: PMC90269
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.1.252-262.2001
Kinetic study of the inflammatory response in Streptococcus pneumoniae experimental pneumonia treated with the ketolide HMR 3004
Abstract
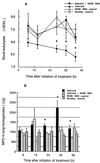
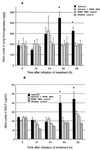
Patients still die from Streptococcus pneumoniae pneumonia after initiation of antibiotic therapy, when tissues are sterile and the pneumonia is clearing. There is growing evidence that overwhelming inflammation resulting from toxin release contributes to tissue injury, shock, and death. Monitoring host response may help us understand the consequences of antibiotic therapy for the inflammatory processes that occur in bacterial pneumonia. HMR 3004 is a ketolide that displays excellent in vitro activity against S. pneumoniae. In the present experiment, we investigated the chronology of inflammatory events that occur during pneumococcal pneumonia in mice treated with HMR 3004. Infection of mice with 10(7) CFU of living S. pneumoniae resulted in 100% mortality within 5 days. HMR 3004 given at 12.5 mg/kg of body weight/dose twice daily from 48 h postinfection achieved complete bacterial clearance from lungs and blood within 36 h and ensured survival of mice. Recruitment of neutrophils and monocytes from blood to lungs was significantly reduced, and nitric oxide release was totally prevented. Interleukin-6 secretion in lungs and blood became rapidly undetectable after initiation of therapy. Histological examination of lung tissue showed protection of interstitium against edema. By controlling bacterial invasion, HMR 3004 led to rapid and profound modifications of the host response in lungs, which may protect mice from deleterious inflammatory reactions.
Figures





References
-
- Bartlett J, Breiman R, Mandell L, File T. Community-acquired pneumonia in adults: guidelines for management. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26:811–838. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron Y, Bergeron M G. Why does pneumococcus kill? Can J Infect Dis. 1999;10(Suppl.):49C–60C.
-
- Dehoux M S, Boutten A, Ostinelli J, Seta N, Dombret M C, Crestani B, Deschenes M, Trouillet J L, Aubier M. Compartmentalized cytokine production within the human lung in unilateral pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;150:710–716. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

