A spectrum of changes occurs in peptidoglycan composition of glycopeptide-intermediate clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates
- PMID: 11120978
- PMCID: PMC90273
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.1.280-287.2001
A spectrum of changes occurs in peptidoglycan composition of glycopeptide-intermediate clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates
Abstract
The mechanism of glycopeptide resistance in Staphylococcus aureus is not known with certainty. Because the target of vancomycin is the D-Ala-D-Ala terminus of the stem peptide of the peptidoglycan precursor, by subjecting muropeptides to reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography, we investigated peptidoglycan obtained from glycopeptide-intermediate S. aureus (GISA) isolates for changes in composition and evaluated whether any peptidoglycan structural change was a consistent feature of clinical GISA isolates. GISA isolates Mu50 and Mu3 from Japan had the large glutamate-containing monomeric peak demonstrated previously, although strain H1, a vancomycin-susceptible MRSA isolate from Japan that was clonally related to Mu3 and Mu50, and a femC mutant that we studied, did also. For the U.S. GISA isolates, strain NJ had a large monomeric peak with a retention time identical to that described for the glutamate-containing monomer in strains H1, Mu3, and Mu50. However, a much smaller corresponding peak was seen in GISA MI, and this peak was absent from both GISA PC and a recent GISA isolate obtained from an adult patient in Illinois (strain IL). These data suggest that a uniform alteration in peptidoglycan composition cannot be discerned among the GISA isolates and indicate that a single genetic or biochemical change is unlikely to account for the glycopeptide resistance phenotype in the clinical GISA isolates observed to date. Furthermore, a large monomeric glutamate-containing peak is not sufficient to confer the resistance phenotype.
Figures
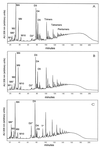
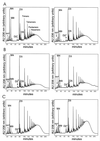
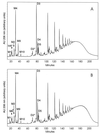
References
-
- Barna J C J, Williams D H. The structure and mode of action of glycopeptide antibiotics of the vancomycin group. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:339–357. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Staphylococcus aureus with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin—Illinois, 1999. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2000;48:1165–1167. - PubMed
-
- CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1997. Staphylococcus aureus with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin—United States, 1997. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 46:765–766. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update: Staphylococcus aureus with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin—United States, Sept. 1997. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1997;46:813–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

