Differential roles for alpha(M)beta(2) integrin clustering or activation in the control of apoptosis via regulation of akt and ERK survival mechanisms
- PMID: 11121444
- PMCID: PMC2190581
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.151.6.1305
Differential roles for alpha(M)beta(2) integrin clustering or activation in the control of apoptosis via regulation of akt and ERK survival mechanisms
Abstract
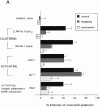
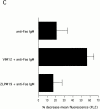
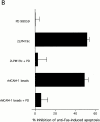
The role of integrins in leukocyte apoptosis is unclear, some studies suggest enhancement, others inhibition. We have found that beta(2)-integrin engagement on neutrophils can either inhibit or enhance apoptosis depending on the activation state of the integrin and the presence of proapoptotic stimuli. Both clustering and activation of alpha(M)beta(2) delays spontaneous, or unstimulated, apoptosis, maintains mitochondrial membrane potential, and prevents cytochrome c release. In contrast, in the presence of proapoptotic stimuli, such as Fas ligation, TNFalpha, or UV irradiation, ligation of active alpha(M)beta(2) resulted in enhanced mitochondrial changes and apoptosis. Clustering of inactive integrins did not show this proapoptotic effect and continued to inhibit apoptosis. This discrepancy was attributed to differential signaling in response to integrin clustering versus activation. Clustered, inactive alpha(M)beta(2) was capable of stimulating the kinases ERK and Akt. Activated alpha(M)beta(2) stimulated Akt, but not ERK. When proapoptotic stimuli were combined with either alpha(M)beta(2) clustering or activation, Akt activity was blocked, allowing integrin activation to enhance apoptosis. Clustered, inactive alpha(M)beta(2) continued to inhibit stimulated apoptosis due to maintained ERK activity. Therefore, beta(2)-integrin engagement can both delay and enhance apoptosis in the same cell, suggesting that integrins can play a dual role in the apoptotic progression of leukocytes.
Figures



















Similar articles
-
Adhesion of neutrophils to fibronectin: role of the cd66 antigens.Cell Immunol. 2001 Mar 15;208(2):96-106. doi: 10.1006/cimm.2001.1772. Cell Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11333142
-
Differential role of beta(1C) and beta(1A) integrin cytoplasmic variants in modulating focal adhesion kinase, protein kinase B/AKT, and Ras/Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Jul;11(7):2235-49. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.7.2235. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10888665 Free PMC article.
-
Laminin-10/11 and fibronectin differentially prevent apoptosis induced by serum removal via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt- and MEK1/ERK-dependent pathways.J Biol Chem. 2002 May 31;277(22):19922-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200383200. Epub 2002 Mar 12. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11891225
-
Dual role of H-Ras in regulation of lymphocyte function antigen-1 activity by stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha: implications for leukocyte transmigration.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Oct;12(10):3074-86. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.10.3074. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11598192 Free PMC article.
-
Human intestinal epithelial crypt cell survival and death: Complex modulations of Bcl-2 homologs by Fak, PI3-K/Akt-1, MEK/Erk, and p38 signaling pathways.J Cell Physiol. 2004 Feb;198(2):209-22. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10399. J Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14603523
Cited by
-
SRC-dependent outside-in signalling is a key step in the process of autoregulation of beta2 integrins in polymorphonuclear cells.Biochem J. 2004 May 15;380(Pt 1):57-65. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040151. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 14969582 Free PMC article.
-
CD11b agonists offer a novel approach for treating lupus nephritis.Transl Res. 2022 Jul;245:41-54. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2022.03.001. Epub 2022 Mar 12. Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35288363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surfactant proteins A and D suppress alveolar macrophage phagocytosis via interaction with SIRP alpha.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008 Jul 15;178(2):158-67. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200711-1661OC. Epub 2008 Apr 17. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18420961 Free PMC article.
-
CD11b activation suppresses TLR-dependent inflammation and autoimmunity in systemic lupus erythematosus.J Clin Invest. 2017 Apr 3;127(4):1271-1283. doi: 10.1172/JCI88442. Epub 2017 Mar 6. J Clin Invest. 2017. PMID: 28263189 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide participates in the induction of brain ischemic tolerance via activating ERK1/2 signaling pathways.Neurochem Res. 2006 Jul;31(7):967-74. doi: 10.1007/s11064-006-9102-2. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Neurochem Res. 2006. PMID: 16847593
References
-
- Alessi D.R., Cuenda A., Cohen P., Dudley D.T., Saltiel A.R. PD 98059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:27489–27494. - PubMed
-
- Altieri D.C. Occupancy of CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1) divalent ion binding site(s) induces leukocyte adhesion. J. Immunol. 1991;147:1891–1898. - PubMed
-
- Bleijs D.A., Binnerts M.E., van Vliet S.J., Figdor C.G., van Kooyk Y. Low-affinity LFA-1/ICAM-3 interactions augment LFA-1/ICAM-1-mediated T cell adhesion and signaling by redistribution of LFA-1. J. Cell Sci. 2000;113:391–400. - PubMed
-
- Chuang P.I., Yee E., Karsan A., Winn R.K., Harlan J.M. A1 is a constitutive and inducible Bcl-2 homologue in mature human neutrophils. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 1998;249:361–365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

