Molecular dynamics studies of the HIV-1 TAR and its complex with argininamide
- PMID: 11121486
- PMCID: PMC115235
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/28.24.4944
Molecular dynamics studies of the HIV-1 TAR and its complex with argininamide
Abstract
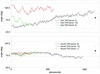
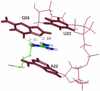
The dynamic behavior of HIV-1 TAR and its complex with argininamide is investigated by means of molecular dynamics simulations starting from NMR structures, with explicit inclusion of water and periodic boundary conditions particle mesh Ewald representation of the electrostatic energy. During simulations of free and argininamide-bound TAR, local structural patterns, as determined by NMR experiments, were reproduced. An interdomain motion was observed in the simulations of free TAR, which is absent in the case of bound TAR, leading to the conclusion that the free conformation of TAR is intrinsically more flexible than the bound conformation. In particular, in the bound conformation the TAR-argininamide interface is very well ordered, as a result of the formation of a U.A.U base triple, which imposes structural constraints on the global conformation of the molecule. Free energy analysis, which includes solvation contributions, was used to evaluate the influence of van der Waals and electrostatic terms on formation of the complex and on the conformational rearrangement from free to bound TAR.
Figures



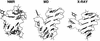


Similar articles
-
Base flexibility in HIV-2 TAR RNA mapped by solution (15)N, (13)C NMR relaxation.J Mol Biol. 2002 Mar 22;317(2):263-78. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5424. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 11902842
-
NMR evidence for a base triple in the HIV-2 TAR C-G.C+ mutant-argininamide complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 1998 Apr 15;26(8):1991-5. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.8.1991. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998. PMID: 9518494 Free PMC article.
-
Argininamide binding arrests global motions in HIV-1 TAR RNA: comparison with Mg2+-induced conformational stabilization.J Mol Biol. 2004 Apr 16;338(1):7-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.02.031. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15050819 Free PMC article.
-
Rational design of inhibitors of HIV-1 TAR RNA through the stabilisation of electrostatic "hot spots".J Mol Biol. 2004 Feb 13;336(2):343-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2003.12.046. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 14757049
-
Discoveries of Tat-TAR interaction inhibitors for HIV-1.Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord. 2005 Dec;5(4):433-44. doi: 10.2174/156800505774912901. Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord. 2005. PMID: 16535863 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure of a low-population binding intermediate in protein-RNA recognition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jun 28;113(26):7171-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1521349113. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27286828 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dynamics reveals the stabilizing role of loop closing residues in kissing interactions: comparison between TAR-TAR* and TAR-aptamer.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jul 15;31(14):4275-84. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg467. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12853646 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dynamics and binding specificity analysis of the bovine immunodeficiency virus BIV Tat-TAR complex.Biophys J. 2001 Jun;80(6):2833-42. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(01)76250-9. Biophys J. 2001. PMID: 11371457 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Mutations in Differential Recognition of Viral RNA Molecules by Peptides.J Chem Inf Model. 2022 Jul 25;62(14):3381-3390. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.2c00376. Epub 2022 Jul 14. J Chem Inf Model. 2022. PMID: 35833626 Free PMC article.
-
The bulge region of HIV-1 TAR RNA binds metal ions in solution.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Oct 1;30(19):4241-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf541. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 12364603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weeks K.M., Ampe,C., Schultz,S.C., Steitz,T.A. and Crothers,D.M. (1990) Science, 249, 1281–1285. - PubMed
-
- Churcher M.J., Lamont,C., Hamy,F., Dingwall,C., Green,S.M., Lowe,A.D., Butler,P.J.G., Gait,M.J. and Karn,J. (1993) J. Mol. Biol., 230, 90–110. - PubMed
-
- Weeks K.M. and Crothers,D.M. (1991) Cell, 66, 577–588. - PubMed
-
- Calnan B.J., Tidor,B., Biancalana,S., Hudson,D. and Frankel,A.D. (1991) Science, 252, 1167–1171. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

