Parasite-mediated down-regulation of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in DA rats
- PMID: 11122258
- PMCID: PMC1905793
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01384.x
Parasite-mediated down-regulation of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in DA rats
Abstract
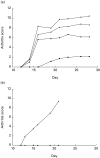
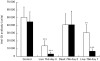
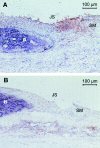
Microbial infection can impact on the course of autoimmune disease, both in disease-inducing and disease-protecting capacities. Here we investigated if infection with Trypanosoma brucei brucei (Tbb), the protozoan causative agent of African Sleeping Sickness, could ameliorate the course of CIA in the Dark Agouti rat, an experimental model which shares many features with human rheumatoid arthritis. Infection of animals with living, but not inoculation with dead Tbb resulted in complete or significant reduction of clinical arthritic symptoms. Infection prior to collagen immunization was more effective than a later treatment, and this effect was related to the level of parasitaemia. Using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction we detected an increase in interferon-gamma mRNA in the draining lymph nodes of Tbb-treated animals relative to controls at day 28 after disease induction. Transforming growth factor-beta could be detected in the lymph nodes in four out of six animals that had received Tbb. In the joints, immunohistochemistry revealed reduced production of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in Tbb-treated animals relative to controls. The most striking difference between Tbb-infected and control groups, as measured by ELISA, was the down-regulation of anti-collagen II IgG antibody responses in parasite-infected animals. We conclude that live parasites can exert an immunomodulatory and protective effect in CIA in which several mechanisms may work in parallel, although the almost complete down-regulation of the anti-collagen antibody response may alone explain the protective effect in CIA. The described model may be useful in further attempts to use the mechanisms involved in parasite immune defence to prevent and treat certain autoimmune conditions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Co-infection with Trypanosoma brucei brucei prevents experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in DBA/1 mice through induction of suppressor APCs.Int Immunol. 2005 Jun;17(6):721-8. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh253. Epub 2005 May 17. Int Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15899926
-
Cytokine profiles in the central nervous system and the spleen during the early course of experimental African trypanosomiasis.Scand J Immunol. 1999 Sep;50(3):256-61. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.1999.00600.x. Scand J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10447934
-
Protection against cartilage and bone destruction by systemic interleukin-4 treatment in established murine type II collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res. 1999;1(1):81-91. doi: 10.1186/ar14. Epub 1999 Oct 26. Arthritis Res. 1999. PMID: 11056663 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen induced arthritis: an experimental model for rheumatoid arthritis with involvement of both DTH and immune complex mediated mechanisms.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1989 Sep-Oct;7 Suppl 3:S51-5. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1989. PMID: 2691160 Review.
-
Role of cytokines in Trypanosoma brucei-induced anaemia: A review of the literature.Malawi Med J. 2015 Jun;27(2):45-50. doi: 10.4314/mmj.v27i2.3. Malawi Med J. 2015. PMID: 26405511 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysing the effect of novel therapies on cytokine expression in experimental arthritis.Int J Exp Pathol. 2005 Oct;86(5):267-78. doi: 10.1111/j.0959-9673.2005.00443.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16191099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of autoimmune arthritis by environmental 'hygiene' and commensal microbiota.Cell Immunol. 2019 May;339:59-67. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.12.005. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Cell Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30638679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antigen inhibition of collagen-induced arthritis is associated with up-regulation of IL-4 mRNA and induction of Ox40 on T cells in draining lymph nodes.Clin Exp Immunol. 2003 Feb;131(2):241-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02054.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12562383 Free PMC article.
-
Review series on helminths, immune modulation and the hygiene hypothesis: how might infection modulate the onset of type 1 diabetes?Immunology. 2009 Jan;126(1):12-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.03009.x. Immunology. 2009. PMID: 19120494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The inhibitory effect against collagen-induced arthritis by Schistosoma japonicum infection is infection stage-dependent.BMC Immunol. 2010 Jun 10;11:28. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-11-28. BMC Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20537152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cole BC, Griffiths MM. Triggering and exacerbation of autoimmune arthritis by the Mycoplasma arthritidis superantigen MAM. Arthritis Rheum. 1993;36:994–1002. - PubMed
-
- Lorentzen JC. Identification of arthritogenic adjuvants of self and foreign origin. Scand J Immunol. 1999;49:45–50. - PubMed
-
- Rook GA, Stanford JL. Give us this day our daily germs. Immunol Today. 1998;19:113–6. - PubMed
-
- Gibbon C, Smith T, Egger P, et al. Early infection and subsequent insulin dependent diabetes. Arch Dis Child. 1997;77:384–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

