Decreased expression levels of L-selectin on subsets of leucocytes and increased serum L-selectin in severe psoriasis
- PMID: 11122259
- PMCID: PMC1905806
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01404.x
Decreased expression levels of L-selectin on subsets of leucocytes and increased serum L-selectin in severe psoriasis
Abstract
L-selectin is a leucocyte adhesion molecule involved in leucocyte interactions with vascular endothelial cells. Following leucocyte activation L-selectin is endoproteolytically released from the cell surface. To assess whether psoriasis vulgaris results in systemic leucocyte activation, we examined expression levels of L-selectin on subsets of peripheral blood leucocytes from patients with psoriasis (n = 25) and normal control subjects. Serum levels of soluble L-selectin were quantified by ELISA in patients with psoriasis (n = 75), pustulosis palmaris et plantaris, and contact dermatitis, as well as normal control subjects. Psoriasis severity was evaluated by psoriasis area and severity index (PASI). L-selectin expression levels on CD4+ T cells, B cells, monocytes, and neutrophils from patients with severe-type psoriasis (PASI > or = 15) was significantly decreased compared with leucocytes from normal control subjects. Furthermore, L-selectin expression on CD4+ T cells showed good inverse correlation with PASI scores. Monocyte L-selectin expression was restored when the skin lesions of psoriasis were remitted. The frequencies of L-selectin+ CD4+ T cells or L-selectin+ CD8+ T cells from patients with psoriasis were almost normal. Serum L-selectin levels in patients with severe-type psoriasis were significantly higher than those in normal control subjects. These results suggest that subsets of leucocytes may be activated in psoriasis, and that L-selectin expression levels on some leucocyte subsets, especially CD4+ T cells, tend to correlate with disease severity of psoriasis.
Figures
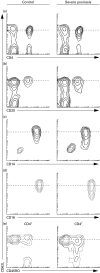



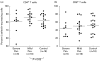
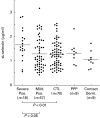
Similar articles
-
Elevated serum L-selectin levels and abnormal regulation of L-selectin expression on leukocytes in atopic dermatitis: soluble L-selectin levels indicate disease severity.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999 Jul;104(1):163-8. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(99)70128-4. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10400854
-
Elevated serum L-selectin levels and decreased L-selectin expression on CD8(+) lymphocytes in systemic sclerosis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2001 Jun;124(3):474-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01514.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11472411 Free PMC article.
-
Methotrexate markedly reduces the expression of vascular E-selectin, cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen and the numbers of mononuclear leucocytes in psoriatic skin.Exp Dermatol. 2004 Jul;13(7):426-34. doi: 10.1111/j.0906-6705.2004.00177.x. Exp Dermatol. 2004. PMID: 15217363
-
Signals regulating L-selectin-dependent leucocyte adhesion and transmigration.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Mar;45(3):550-5. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.12.023. Epub 2013 Jan 5. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23299028 Review.
-
L-selectin: adhesion, signalling and its importance in pathologic posttraumatic endotoxemia and non-septic inflammation.Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2005 Aug;57(1):39-52. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2005.02.007. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16089318 Review.
Cited by
-
CD19+ B cell subsets in the peripheral blood and skin lesions of psoriasis patients and their correlations with disease severity.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2016 Aug 15;49(9):e5374. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20165374. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2016. PMID: 27532281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nickoloff BJ. The immunologic and genetic basis of psoriasis. Arch Dermatol. 1999;135:1104–10. - PubMed
-
- van de Kerkhof PCM. Intraepidermal accumulation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in chronic stable plaque psoriasis. Dermatologica. 1987;174:224–7. - PubMed
-
- van den Oord J, De Wlf-Peeters C. Epithelium-lining macrophages in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1994;130:589–94. - PubMed
-
- Tedder TF, Li X, Steeber DA. The selectins and their ligands: adhesion molecules of the vasculature. Adv Mol Cell Biol. 1999;28:65–111.
-
- Spertini O, Luscinskas FW, Kansas GS, Munro JM, Griffin JD, Gimbrone Ma, Jr, Tedder TF. Leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (LAM-1, L-selectin) interacts with an inducible endothelial cell ligand to support leukocyte adhesion. J Immunol. 1991;147:2565–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

