DCAMKL1 encodes a protein kinase with homology to doublecortin that regulates microtubule polymerization
- PMID: 11124993
- PMCID: PMC6773030
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-24-09152.2000
DCAMKL1 encodes a protein kinase with homology to doublecortin that regulates microtubule polymerization
Abstract
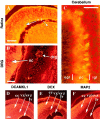
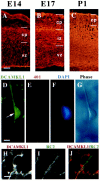
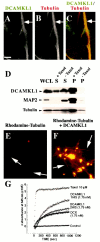
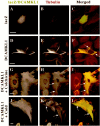
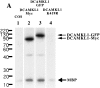
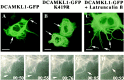
Doublecortin (DCX) is a microtubule-associated protein required for neuronal migration to the cerebral cortex. DCAMKL1 consists of an N terminus that is 65% similar to DCX throughout the entire length of DCX, but also contains an additional 360 amino acid C-terminal domain encoding a putative Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. The homology to DCX suggested that DCAMKL1 may regulate microtubules, as well as mediate a phosphorylation-dependent signal transduction pathway. Here we show that DCAMKL1 is expressed throughout the CNS and PNS in migrating neuronal populations and overlaps in its expression with DCX and microtubules. Purified DCAMKL1 associates with microtubules and stimulates polymerization of purified tubulin and the formation of aster-like microtubule structures. Overexpressed DCAMKL1 leads to striking microtubule bundling in cell lines and cultured primary neural cells. Time-lapse imaging of cells transfected with a DCAMKL1-green fluorescent protein fusion protein shows that the microtubules associated with the protein remain dynamic. DCAMKL1 also encodes a functional kinase capable of phosphorylating myelin basic protein and itself. However, elimination of the kinase activity of DCAMKL1 has no detectable effect on its microtubule polymerization activity. Because DCAMKL1 is coexpressed with DCX, the two proteins form a potentially mutually regulatory network linking calcium signaling and microtubule dynamics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Doublecortin-like kinase is associated with microtubules in neuronal growth cones.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2000 Nov;16(5):529-41. doi: 10.1006/mcne.2000.0891. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11083916
-
DCAMKL1, a brain-specific transmembrane protein on 13q12.3 that is similar to doublecortin (DCX).Genomics. 1999 Feb 15;56(1):121-6. doi: 10.1006/geno.1998.5718. Genomics. 1999. PMID: 10036192
-
The DCX-domain tandems of doublecortin and doublecortin-like kinase.Nat Struct Biol. 2003 May;10(5):324-33. doi: 10.1038/nsb918. Nat Struct Biol. 2003. PMID: 12692530
-
DCX's phosphorylation by not just another kinase (JNK).Cell Cycle. 2004 Jun;3(6):747-51. Epub 2004 Jun 6. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 15118415 Review.
-
Doublecortin functions at the extremities of growing neuronal processes.Cereb Cortex. 2003 Jun;13(6):620-6. doi: 10.1093/cercor/13.6.620. Cereb Cortex. 2003. PMID: 12764037 Review.
Cited by
-
APSA Awardee Submission: Tumor/cancer stem cell marker doublecortin-like kinase 1 in liver diseases.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Feb;242(3):242-249. doi: 10.1177/1535370216672746. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 27694285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional genomic analysis of oligodendrocyte differentiation.J Neurosci. 2006 Oct 25;26(43):10967-83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2572-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17065439 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and prognostic significance of doublecortin-like kinase 1 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2017 Dec;14(6):7529-7537. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7082. Epub 2017 Sep 27. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29344199 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome assessment of the retinal response to diabetes reveals a progressive neurovascular inflammatory response.BMC Med Genomics. 2008 Jun 13;1:26. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-1-26. BMC Med Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18554398 Free PMC article.
-
Doublecortin-like kinase 1 promotes hepatocyte clonogenicity and oncogenic programming via non-canonical β-catenin-dependent mechanism.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 29;10(1):10578. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67401-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32601309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anton ES, Kreidberg JA, Rakic P. Distinct functions of alpha3 and alpha(v) integrin receptors in neuronal migration and laminar organization of the cerebral cortex. Neuron. 1999;22:277–289. - PubMed
-
- Avila J, Dominguez J, Diaz-Nido J. Regulation of microtubule dynamics by microtubule-associated protein expression and phosphorylation during neuronal development. Int J Dev Biol. 1994;38:13–25. - PubMed
-
- Baas PW. Microtubules and neuronal polarity: lessons from mitosis. Neuron. 1999;22:23–31. - PubMed
-
- Benezra R, Davis RL, Lockshon D, Turner DL, Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990;61:49–59. - PubMed
-
- Berg MJ, Schifitto G, Powers JM, Martinez-Capolino C, Fong CT, Myers GJ, Epstein LG, Walsh CA. X-linked female band heterotopia-male lissencephaly syndrome. Neurology. 1998;50:1143–1146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
