Slope analysis of the optic disc in eyes with ocular hypertension and early normal tension glaucoma by confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope
- PMID: 11133713
- PMCID: PMC1723693
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.85.1.56
Slope analysis of the optic disc in eyes with ocular hypertension and early normal tension glaucoma by confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope
Abstract
Aims: To determine whether quantitative differences in sector based slope can differentiate between eyes with ocular hypertension with and without glaucomatous disc changes and eyes with normal tension glaucoma with glaucomatous disc changes.
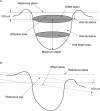
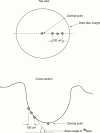
Methods: Seventy six eyes with ocular hypertension or early glaucomatous disc changes were consecutively categorised into three groups: 22 eyes with ocular hypertension and no glaucomatous disc changes (OHND); 35 with ocular hypertension and glaucomatous disc changes (OHD); and 19 with normal ocular tension and glaucomatous disc changes (NTD). Twenty eyes served as controls. The average total slope angle and sector based slope angle of the cup, total contour area, effective area, neuroretinal rim area, half depth area, cup to disc ratio, contour variation, mean contour depth, average depth, volume below, half depth volume, and contour tilt were evaluated with a confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope.
Results: The earliest changes in eyes with OHND or OHD started in the slope at the nasal inferior sector (p<0.05), followed by the superior and temporal superior sectors (p<0.05). The mean slopes in eyes with NTD and OHD were steeper than in controls (p<0.05). Statistically significant differences were found between controls and disease groups in the half depth area, mean contour depth, and half depth volume. The cup to disc ratios in eyes with OHD and NTD were greater than in eyes with OHND; the volume below was greater in eyes with NTD than in eyes with OHND and OHD.
Conclusions: The steep slope in the nasal inferior section is the first indicator of glaucomatous nerve defects in many eyes. The half depth parameters, half depth area, and half depth volume may be useful for distinguishing ocular hypertension with and without glaucomatous disc changes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optic nerve head topography in ocular hypertensive eyes using confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy.Am J Ophthalmol. 1996 Oct;122(4):520-5. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)72112-9. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996. PMID: 8862049
-
[Optic nerve head parameters as measured by confocal scanning laser (Heidelberg Retina Tomograph II) in normal, ocular hypertensive and glaucomatous subjects].Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2008 Jul;83(7):407-15. doi: 10.4321/s0365-66912008000700004. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2008. PMID: 18592440 Clinical Trial. Spanish.
-
Racial differences in optic disc topography: baseline results from the confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy ancillary study to the ocular hypertension treatment study.Arch Ophthalmol. 2004 Jan;122(1):22-8. doi: 10.1001/archopht.122.1.22. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004. PMID: 14718290 Clinical Trial.
-
Reproducibility of topometric data acquisition in normal and glaucomatous optic nerve heads with the laser tomographic scanner.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1993 Aug;231(8):457-64. doi: 10.1007/BF02044232. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1993. PMID: 8224945 Review.
-
Advances in the assessment of optic disc changes in early glaucoma.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1995 Apr;6(2):61-6. doi: 10.1097/00055735-199504000-00010. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1995. PMID: 10150859 Review.
Cited by
-
Optic nerve head slope-based quantitative parameters for identifying open-angle glaucoma on SPECTRALIS OCT images.Int Ophthalmol. 2017 Aug;37(4):979-988. doi: 10.1007/s10792-016-0362-9. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Int Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 27682504
-
Optic cup morphology associated with glaucomatous damage: Findings from the Primary Open-Angle African American Glaucoma Genetics (POAAGG) Study.AJO Int. 2024 Oct 3;1(3):100053. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoint.2024.100053. Epub 2024 Jul 14. AJO Int. 2024. PMID: 39989596 Free PMC article.
-
Common variants on chromosome 9p21 are associated with normal tension glaucoma.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040107. Epub 2012 Jul 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22792221 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of rat and mouse RGC apoptosis imaging in vivo with different scanning laser ophthalmoscopes.Curr Eye Res. 2007 Oct;32(10):851-61. doi: 10.1080/02713680701585872. Curr Eye Res. 2007. PMID: 17963105 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of the long-term effects of dorzolamide 2% and brinzolamide 1%, each added to timolol 0.5%, on retrobulbar hemodynamics and intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma patients.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Jun;25(3):239-48. doi: 10.1089/jop.2008.0114. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19348600 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
