Wee1-regulated apoptosis mediated by the crk adaptor protein in Xenopus egg extracts
- PMID: 11134069
- PMCID: PMC2150666
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.151.7.1391
Wee1-regulated apoptosis mediated by the crk adaptor protein in Xenopus egg extracts
Abstract
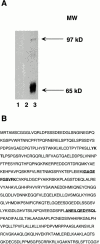
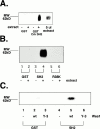
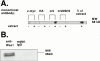
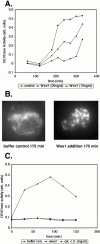
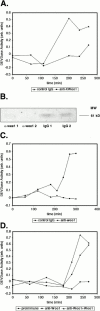
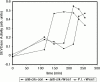
Many of the biochemical reactions of apoptotic cell death, including mitochondrial cytochrome c release and caspase activation, can be reconstituted in cell-free extracts derived from Xenopus eggs. In addition, because caspase activation does not occur until the egg extract has been incubated for several hours on the bench, upstream signaling processes occurring before full apoptosis are rendered accessible to biochemical manipulation. We reported previously that the adaptor protein Crk is required for apoptotic signaling in egg extracts (Evans, E.K., W. Lu, S.L. Strum, B.J. Mayer, and S. Kornbluth. 1997. EMBO (Eur. Mol. Biol. Organ.) J. 16:230-241). Moreover, we demonstrated that removal of Crk Src homology (SH)2 or SH3 interactors from the extracts prevented apoptosis. We now report the finding that the relevant Crk SH2-interacting protein, important for apoptotic signaling in the extract, is the well-known cell cycle regulator, Wee1. We have demonstrated a specific interaction between tyrosine-phosphorylated Wee1 and the Crk SH2 domain and have shown that recombinant Wee1 can restore apoptosis to an extract depleted of SH2 interactors. Moreover, exogenous Wee1 accelerated apoptosis in egg extracts, and this acceleration was largely dependent on the presence of endogenous Crk protein. As other Cdk inhibitors, such as roscovitine and Myt1, did not act like Wee1 to accelerate apoptosis, we propose that Wee1-Crk complexes signal in a novel apoptotic pathway, which may be unrelated to Wee1's role as a cell cycle regulator.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Crk is required for apoptosis in Xenopus egg extracts.EMBO J. 1997 Jan 15;16(2):230-41. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.2.230. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9029144 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic regulation by the Crk adapter protein mediated by interactions with Wee1 and Crm1/exportin.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Mar;22(5):1412-23. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.5.1412-1423.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11839808 Free PMC article.
-
B cell antigen receptor signaling induces the formation of complexes containing the Crk adapter proteins.J Biol Chem. 1996 Dec 13;271(50):32306-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.50.32306. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8943292
-
SH2 and SH3-containing adaptor proteins: redundant or independent mediators of intracellular signal transduction.Genes Cells. 1996 Jul;1(7):595-613. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.1996.00258.x. Genes Cells. 1996. PMID: 9078388 Review.
-
Crk family adaptors-signalling complex formation and biological roles.Oncogene. 2001 Oct 1;20(44):6348-71. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204779. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11607838 Review.
Cited by
-
CRK SH3N Domain Diminishes Cell Invasiveness of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Genes Cancer. 2013 Jul;4(7-8):315-24. doi: 10.1177/1947601913497573. Genes Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24167658 Free PMC article.
-
Crk and CrkL adaptor proteins: networks for physiological and pathological signaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2009 May 10;7:13. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-7-13. Cell Commun Signal. 2009. PMID: 19426560 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of cryptochrome reduces cancer risk in p53 mutant mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Feb 24;106(8):2841-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813028106. Epub 2009 Feb 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19188586 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Translocation of Crk Adaptor Proteins by the Influenza A Virus NS1 Protein.Viruses. 2016 Apr 15;8(4):101. doi: 10.3390/v8040101. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27092521 Free PMC article.
-
Depletion of Wee-1 kinase is necessary for both human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpr- and gamma irradiation-induced apoptosis.J Virol. 2003 Feb;77(3):2063-70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.3.2063-2070.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12525641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alnemri E.S. Mammalian cell death proteasesa family of highly conserved aspartate specific cysteine proteases. J. Cell. Biochem. 1997;64:33–42. - PubMed
-
- Birge R.B., Knudsen B.S., Besser D., Hanafusa H. SH2 and SH3-containing adaptor proteinsredundant or independent mediators of intracellular signal transduction. Genes Cells. 1996;1:595–613. - PubMed
-
- Coleman T.R., Dunphy W.G. Cdc2 regulatory factors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1994;6:877–882. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

