Metaphase to anaphase (mat) transition-defective mutants in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 11134076
- PMCID: PMC2150685
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.151.7.1469
Metaphase to anaphase (mat) transition-defective mutants in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
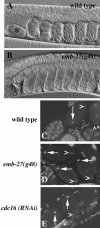
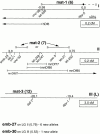
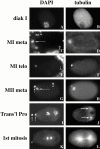
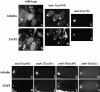
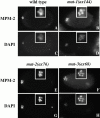
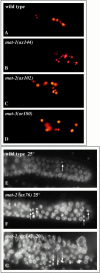
The metaphase to anaphase transition is a critical stage of the eukaryotic cell cycle, and, thus, it is highly regulated. Errors during this transition can lead to chromosome segregation defects and death of the organism. In genetic screens for temperature-sensitive maternal effect embryonic lethal (Mel) mutants, we have identified 32 mutants in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans in which fertilized embryos arrest as one-cell embryos. In these mutant embryos, the oocyte chromosomes arrest in metaphase of meiosis I without transitioning to anaphase or producing polar bodies. An additional block in M phase exit is evidenced by the failure to form pronuclei and the persistence of phosphohistone H3 and MPM-2 antibody staining. Spermatocyte meiosis is also perturbed; primary spermatocytes arrest in metaphase of meiosis I and fail to produce secondary spermatocytes. Analogous mitotic defects cause M phase delays in mitotic germline proliferation. We have named this class of mutants "mat" for metaphase to anaphase transition defective. These mutants, representing six different complementation groups, all map near genes that encode subunits of the anaphase promoting complex or cyclosome, and, here, we show that one of the genes, emb-27, encodes the C. elegans CDC16 ortholog.
Figures




References
-
- Albertson D.G. Formation of the first cleavage spindle in nematode embryos. Dev. Biol. 1984;101:61–72. - PubMed
-
- Albertson D.G., Thomson J.N. Segregation of holocentric chromosomes at meiosis in the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans . Chromosome Res. 1993;1:15–26. - PubMed
-
- Altschul S.F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E.W., Lipman D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Beanan M.J., Strome S. Characterization of a germ-line proliferation mutation in C. elegans . Development. 1992;116:755–766. - PubMed
-
- Blatch G.L., Lassle M. The tetratricopeptide repeata structural motif mediating protein-protein interactions. Bioessays. 1999;21:932–939. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

