Activated R-ras, Rac1, PI 3-kinase and PKCepsilon can each restore cell spreading inhibited by isolated integrin beta1 cytoplasmic domains
- PMID: 11134082
- PMCID: PMC2150687
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.151.7.1549
Activated R-ras, Rac1, PI 3-kinase and PKCepsilon can each restore cell spreading inhibited by isolated integrin beta1 cytoplasmic domains
Abstract
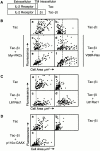
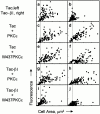
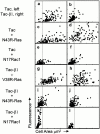
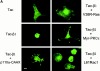
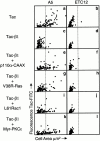
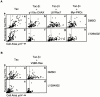
Attachment of many cell types to extracellular matrix proteins triggers cell spreading, a process that strengthens cell adhesion and is a prerequisite for many adhesion-dependent processes including cell migration, survival, and proliferation. Cell spreading requires integrins with intact beta cytoplasmic domains, presumably to connect integrins with the actin cytoskeleton and to activate signaling pathways that promote cell spreading. Several signaling proteins are known to regulate cell spreading, including R-Ras, PI 3-kinase, PKCepsilon and Rac1; however, it is not known whether they do so through a mechanism involving integrin beta cytoplasmic domains. To study the mechanisms whereby cell spreading is regulated by integrin beta cytoplasmic domains, we inhibited cell spreading on collagen I or fibrinogen by expressing tac-beta1, a dominant-negative inhibitor of integrin function, and examined whether cell spreading could be restored by the coexpression of either V38R-Ras, p110alpha-CAAX, myr-PKCepsilon, or L61Rac1. Each of these activated signaling proteins was able to restore cell spreading as assayed by an increase in the area of cells expressing tac-beta1. R-Ras and Rac1 rescued cell spreading in a GTP-dependent manner, whereas PKCstraightepsilon required an intact kinase domain. Importantly, each of these signaling proteins required intact beta cytoplasmic domains on the integrins mediating adhesion in order to restore cell spreading. In addition, the rescue of cell spreading by V38R-Ras was inhibited by LY294002, suggesting that PI 3-kinase activity is required for V38R-Ras to restore cell spreading. In contrast, L61Rac1 and myr-PKCstraightepsilon each increased cell spreading independent of PI 3-kinase activity. Additionally, the dominant-negative mutant of Rac1, N17Rac1, abrogated cell spreading and inhibited the ability of p110alpha-CAAX and myr-PKCstraightepsilon to increase cell spreading. These studies suggest that R-Ras, PI 3-kinase, Rac1 and PKCepsilon require the function of integrin beta cytoplasmic domains to regulate cell spreading and that Rac1 is downstream of PI 3-kinase and PKCepsilon in a pathway involving integrin beta cytoplasmic domain function in cell spreading.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differential role of beta(1C) and beta(1A) integrin cytoplasmic variants in modulating focal adhesion kinase, protein kinase B/AKT, and Ras/Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Jul;11(7):2235-49. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.7.2235. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10888665 Free PMC article.
-
A functional comparison of mutations in integrin beta cytoplasmic domains: effects on the regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation, cell spreading, cell attachment and beta1 integrin conformation.J Cell Sci. 2001 Aug;114(Pt 15):2795-807. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.15.2795. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11683413
-
The NPIY motif in the integrin beta1 tail dictates the requirement for talin-1 in outside-in signaling.J Cell Sci. 2010 Apr 15;123(Pt 8):1216-26. doi: 10.1242/jcs.056549. Epub 2010 Mar 23. J Cell Sci. 2010. PMID: 20332112 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the cytokinesis cleavage furrow by PKCε.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Dec;42(6):1534-7. doi: 10.1042/BST20140240. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 25399566 Review.
-
PI3Kα in cardioprotection: Cytoskeleton, late Na+ current, and mechanism of arrhythmias.Channels (Austin). 2019 Dec;13(1):520-532. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2019.1697127. Channels (Austin). 2019. PMID: 31790629 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of H-Ras-driven MAPK signaling, transformation and tumorigenesis, but not PI3K signaling and tumor progression, by plasma membrane microdomains.Oncogenesis. 2016 May 30;5(5):e228. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2016.36. Oncogenesis. 2016. PMID: 27239960 Free PMC article.
-
H-Ras, R-Ras, and TC21 differentially regulate ureteric bud cell branching morphogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Apr;17(4):2046-56. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-08-0800. Epub 2006 Feb 8. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16467383 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of basal lateral membrane mobility and permeability to divalent cations by membrane associated-protein kinase C.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 8;8(11):e80291. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080291. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24260363 Free PMC article.
-
Tac-beta1 inhibits FAK activation and Src signaling.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Mar 28;368(1):62-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.01.034. Epub 2008 Jan 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18198129 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase C family: on the crossroads of cell signaling in skin and tumor epithelium.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2007 Nov;133(11):793-808. doi: 10.1007/s00432-007-0280-3. Epub 2007 Jul 28. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17661083 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burridge K., Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M. Focal adhesions, contractility, and signaling. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1996;12:463–519. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y.-P., O'Toole T.E., Shipley T., Forsyth J., LaFlamme S.E., Yamada K.M., Shattil S.J., Ginsberg M.H. “Inside-out” signal transduction inhibited by isolated integrin cytoplasmic domains. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:18307–18310. - PubMed
-
- Chou M.M., Hou W., Johnson J., Graham L.K., Lee M.H., Chen C.-S., Newton A.C., Schaffhausen B.S., Toker A. Regulation of protein kinase C ζ by PI 3-kinase and PDK-1. Curr. Biol. 1998;8:1069–1077. - PubMed
-
- Chun J.-S., Ha M.-J., Jacobson B.S. Differential translocation of protein kinase C ε during HeLa cell adhesion to a gelatin substratum. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:13008–13012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

