Genetic analysis for virulence factors in Escherichia coli O104:H21 that was implicated in an outbreak of hemorrhagic colitis
- PMID: 11136742
- PMCID: PMC87673
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.1.24-28.2001
Genetic analysis for virulence factors in Escherichia coli O104:H21 that was implicated in an outbreak of hemorrhagic colitis
Abstract
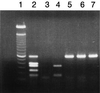
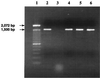
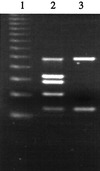
Isolates of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) of serotype O104:H21 implicated in a 1994 outbreak of hemorrhagic colitis in Montana were analyzed for the presence of trait EHEC virulence markers. By using a multiplex PCR that specifically amplifies several genes, the O104:H21 strains were found to carry only the Shiga toxin 2 gene (stx2) and to express Stx2. They did not have the eaeA gene for gamma-intimin, which is typically found in O157:H7, or the alpha- or beta-intimin derivatives, which are common in other EHEC and enteropathogenic E. coli serotypes. Results of the multiplex PCR also indicated that the ehxA gene for enterohemolysin was absent from O104:H21. This, however, was not consistent with the results of a phenotypic assay that showed them to be hemolytic or a PCR analysis with another set of ehxA-specific primers, which indicated the presence of ehxA. To resolve this discrepancy, the ehxA region in O104:H21 and O157:H7 strains, to which the multiplex PCR primers anneal, was cloned and sequenced. Comparison of the sequences showed that the upstream primer binding site in the ehxA gene of O104:H21 was not identical to that of O157:H7. Specifically, there were several base mutations, including an A-to-G substitution at the 3' end of the primer binding site. These base mutations are presumably not unique to O104:H21, since other enterohemolytic serotypes were also not detected with the ehxA primers used in the multiplex PCR. Comparison of the ehxA sequences of O104:H21 strains with those of other Stx-producing E. coli strains showed that they more closely resembled those of O8:H19 strains, which have cluster II ehxA genes, than those of O157:H7 strains, which have cluster I ehxA sequences. By modifying the upstream ehxA primer, the multiplex PCR was able to detect ehxA genes in both O157:H7 and O104:H21 strains.
Figures

References
-
- Barrettt T J, Kaper J B, Jerse A E, Wachsmuth I K. Virulence factors in Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from humans and cattle. J Infect Dis. 1992;165:979–980. - PubMed
-
- Bettelheim K A. Identification of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli by means of their production of enterohaemolysin. J Appl Bacteriol. 1995;79:178–180. - PubMed
-
- Beutin L, Aleksic S, Zimmermann S, Gleier K. Virulence factors and phenotypic traits of verotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli isolated from human patients in Germany. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1994;183:13–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

